Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2) disease, tripeptidyl peptidase 1 (TPP1) deficiency
Active Ingredient: Cerliponase alfa
Indication for Cerliponase alfa
Cerliponase alfa is indicated for the treatment of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2) disease, also known as tripeptidyl peptidase 1 (TPP1) deficiency.
For this indication, competent medicine agencies globally authorize below treatments:
100-300 mg every other week
Route of admnistration
Intracisternal
Defined daily dose
100 - 300 mg
Dosage regimen
From 100 To 300 mg once every 14 day(s)
Detailed description
The safety and efficacy of cerliponase alfa in children less than 3 years of age has not yet been established. Limited data are available for children aged 2 years and no clinical data is available in children below 2 years of age. The posology proposed in children below 2 years has been estimated based on brain mass.
Treatment of cerliponase alfa was initiated in children 2 to 8 years of age in clinical studies. There is limited data in patients older than 8 years of age. Treatment should be based on the benefits and risks to the individual patient as assessed by the physician.
The posology selected for patients is based on age at time of treatment and should be adjusted accordingly (see Table 1). In patients less than 3 years of age the recommended dose is in accordance with the posology used in the ongoing clinical study 190-203.
Table 1. Dose and volume of cerliponase alfa:
| Age groups | Total dose administered every other week (mg) | Volume of cerliponase alfa solution (ml) |
|---|---|---|
| Birth to <6 months | 100 | 3.3 |
| 6 months to <1 year | 150 | 5 |
| 1 year to <2 years | 200 (first 4 doses) | 6.7 (first 4 doses) |
| 300 (subsequent doses) | 10 (subsequent doses) | |
| 2 years and older | 300 | 10 |
Dose adjustments
Consideration of dose adjustments may be necessary for patients who may not tolerate the infusion. The dose may be reduced by 50% and/or the infusion rate decreased to a slower rate.
If the infusion is interrupted due to a hypersensitivity reaction, it should be restarted at approximately one- half the initial infusion rate at which the hypersensitivity reaction occurred.
The infusion should be interrupted and/or the rate slowed in patients who in the judgement of the treating physician have a possible increase in intracranial pressure during the infusion as suggested by symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, or decreased mental state. These precautions are of particular importance in patients below 3 years of age.
Dosage considerations
Intracerebroventricular use.
Precautions to be taken before handling or administering the medicinal product
Aseptic technique must be strictly observed during preparation and administration.
Cerliponase alfa and the flushing solution must only be administered by the intracerebroventricular route. Each vial of Cerliponase alfa and flushing solution are intended for single use only.
Cerliponase alfa is administered to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by infusion via a surgically implanted reservoir and catheter (intracerebroventricular access device). The intracerebroventricular access device must be implanted prior to the first infusion. The implanted intracerebroventricular access device should be appropriate for accessing the cerebral ventricles for therapeutic administration.
Following Cerliponase alfa infusion, a calculated amount of flushing solution must be used to flush the infusion components including the intracerebroventricular access device in order to fully administer Cerliponase alfa and to maintain patency of the intracerebroventricular access device. Cerliponase alfa and flushing solution vials should be thawed prior to administration. The infusion rate for Cerliponase alfa and the flushing solution is 2.5 ml/hour. The complete infusion time, including Cerliponase alfa and the required flushing solution, is approximately 2 to 4.5 hours, depending on the dose and volume administered.
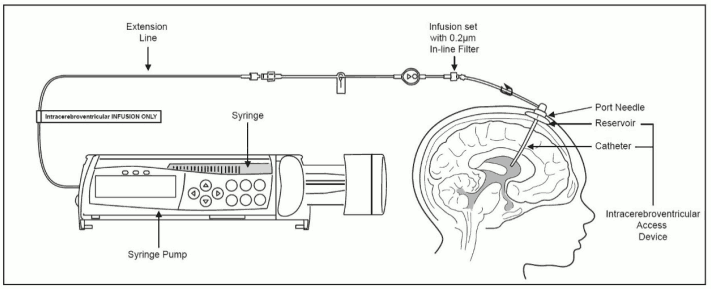
Intracerebroventricular Infusion of Cerliponase alfa
Administer Cerliponase alfa before the flushing solution.
1. Label the infusion line for “Intracerebroventricular infusion only”.
2. Attach the syringe containing Cerliponase alfa to the extension line, if used, otherwise connect the syringe to the infusion set. The infusion set must be equipped with a 0.2 μm inline filter. See Figure 1.
3. Prime the infusion components with Cerliponase alfa.
4. Inspect the scalp for signs of intracerebroventricular access device leakage or failure and for potential infections. Do not administer Cerliponase alfa if there are signs and symptoms of acute intracerebroventricular access device leakage, device failure, or device-related infection.
5. Prepare the scalp for intracerebroventricular infusion using aseptic technique per institution standard of care.
6. Insert the port needle into the intracerebroventricular access device.
7. Connect a separate empty sterile syringe (no larger than 3 ml) to the port needle. Withdraw 0.5 ml to 1 ml of CSF to check patency of the intracerebroventricular access device.
- Do not return CSF to the intracerebroventricular access device. CSF samples should routinely be sent for infection monitoring.
8. Attach the infusion set to the port needle.
- Secure the components per institution standard of care.
9. Place the syringe containing Cerliponase alfa into the syringe pump and program the pump to deliver at an infusion rate of 2.5 ml per hour.
- Program the pump alarms to sound at the most sensitive settings for pressure, rate, and volume limits. See the syringe pump manufacturer’s operating manual for details.
- Do not deliver as a bolus or manually.
10. Initiate infusion of Cerliponase alfa at a rate of 2.5 ml per hour.
11. Periodically inspect the infusion system during the infusion for signs of leakage or delivery failure.
12. Verify that the “Cerliponase alfa” syringe in the syringe pump is empty after the infusion is complete. Detach and remove the empty syringe from the pump and disconnect from the tubing. Discard the empty syringe in accordance with local requirements.
Figure 1. Infusion System Set Up:
Intracerebroventricular infusion of the flushing solution
Administer the flushing solution provided after the Cerliponase alfa infusion is complete.
1. Attach the syringe containing the calculated volume of flushing solution to the infusion components.
2. Place the syringe containing the flushing solution into the syringe pump and program the pump to deliver an infusion rate of 2.5 ml per hour.
Program the pump alarms to sound at the most sensitive settings for pressure, rate, and volume limits. See the syringe pump manufacturer’s operating manual for details.
- Do not deliver as a bolus or manually.
3. Initiate infusion of the flushing solution at a rate of 2.5 ml per hour.
4. Periodically inspect the infusion components during the infusion for signs of leakage or delivery failure.
5. Verify that the “flushing solution” syringe in the syringe pump is empty after the infusion is complete. Detach and remove the empty syringe from the pump and disconnect from the infusion line.
6. Remove the port needle. Apply gentle pressure and bandage the infusion site per institution standard of care.
7. Dispose of the infusion components, needles, unused solutions and other waste materials in accordance with local requirements.
Liability Disclaimer : RxReasoner has utilized reasonable care in providing content and services that are accurate, complete and up to date. However, RxReasoner does not accept any responsibility or liability about it. The content and services of RxReasoner are for informational purposes only and they are not intended to be a substitute for the knowledge, expertise, skill, and judgment of physicians, pharmacists, nurses, or other healthcare professionals involved in patient care. RxReasoner offers no medical advice. Users are responsible for the use of the provided content. A shown indication or treatment should not be construed to indicate that the medication is safe, appropriate, or effective in any given patient or under any particular circumstances. The absence of an indication or treatment should not roule out the existence of other appropriate medications. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or medicament. RxReasoner is not liable for any damages allegedly sustained arising out of the use of its content and services.