KORJUNY Concentrate for solution for infusion Ref.[114664] Active ingredients: Catumaxomab
Source: European Medicines Agency (EU) Revision Year: 2025 Publisher: Lindis Biotech GmbH, Zeppelinstraße 4, 82178 Puchheim, Germany
4.1. Therapeutic indications
Korjuny is indicated for the intraperitoneal treatment of malignant ascites in adults with epithelial cellular adhesion molecule (EpCAM)-positive carcinomas, who are not eligible for further systemic anticancer therapy.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Korjuny must be administered under the supervision of a physician experienced in the use of anti-cancer medicinal products
pCAM testing
EpCAM positivity (≥400 EpCAM-positive cells/106 analysed ascites cells) should be assessed by a CE-marked IVD with the corresponding intended purpose. If the CE-marked IVD is not available, an alternative validated test should be used (see section 5.1).
Posology
Prior to the intraperitoneal infusion, medication for the prophylactic treatment of cytokine release symptoms, including analgesic, antipyretic and non-steroidal antiphlogistic medicinal products is recommended (see sections 4.4 and 5.1).
Side effects of catumaxomab treatment should be treated as medically indicated and according to the current standard of care.
Korjuny dosing schedule comprises the 4 intraperitoneal infusions listed in table 1.
Table 1. Korjuny dosing schedule:
| Infusion number | Dose | Day |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 micrograms | 0 |
| 2 | 20 micrograms | 3 |
| 3 | 50 micrograms | 7 |
| 4 | 150 micrograms | 10 |
Patients should remain under close medical supervision for at least 24 hours after the first infusion of Korjuny. For the remaining doses, patients may be hospitalised for at least 6 hours or for a longer time after infusions of Korjuny at the discretion of the treating physician to safeguard patient safety.
The interval between the infusion days can be prolonged at the discretion of the treating physician if needed in order to minimise the risk of adverse reactions. The overall treatment period should not exceed 21 days.
Special populations
Hepatic impairment
No dose adjustment is needed for patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Patients with severe hepatic impairment and/or with more than 70% of the liver metastasised and/or portal vein thrombosis/obstruction have not been investigated. Treatment of these patients with Korjuny should only be considered after a thorough evaluation of benefit/risk (see sections 4.4 and 5.2).
Renal impairment
No dose adjustment is needed for patients with mild renal impairment. Patients with moderate to severe renal impairment have not been studied. Treatment of these patients with Korjuny should only be considered after a thorough evaluation of benefit/risk (see sections 4.4 and 5.2).
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of Korjuny in children aged less than 18 years have not been established. No data are available.
Method of administration
Korjuny must be administered as an intraperitoneal infusion only. Korjuny must not be administered by intraperitoneal bolus or by any other route of administration. For information on the perfusion system to be used see section 6.5.
Korjuny has to be administered as constant rate intraperitoneal infusion with an infusion time of at least 3 hours. In clinical studies infusion times of 3 hours and 6 hours were investigated. For the first of the 4 doses, an infusion time of 6 hours may be considered depending on the patient’s health condition.
Precautions to be taken before administering the medicinal product
Before administration of Korjuny, the concentrate for solution for infusion is diluted in sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection. The diluted KORJUNY solution for infusion is administered intraperitoneally as constant rate infusion using an adequate pump system.
For instructions on dilution of the medicinal product before administration, see section 6.6.
4.9. Overdose
Symptoms
Higher planned doses of catumaxomab were investigated in dose escalation studies, up to single treatment courses of catumaxomab 10-20-50-200-200 micrograms. Overall, effects observed with catumaxomab doses higher than the proposed dose were in line with known adverse reactions associated with catumaxomab administration and its mechanism of action. Laboratory values, notably changes in liver parameters, showed transient increases that were dose-dependent and showed tendency to accumulate.
Treatment
No antidote for catumaxomab is available. In case of overdose, symptomatic treatment should be initiated at the physician’s discretion.
6.3. Shelf life
2 years.
After dilution:
The prepared solution for infusion is physically and chemically stable for 48 hours at 2°C to 8°C and for 24 hours at a temperature not above 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions prior to use are the responsibility of the user and would normally not be longer than 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C, unless dilution has taken place in controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
6.4. Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2°C-8°C).
Do not freeze.
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
For storage conditions after dilution of the medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5. Nature and contents of container
Pre-filled syringe (type I glass, siliconised) with plunger stopper (bromobutyl rubber) and luer lock system (polypropylene siliconised and polycarbonate), with tip cap (bromobutyl rubber). A cannula is enclosed.
Korjuny 10 micrograms concentrate for solution for infusion:
The pre-filled syringe contains 0.1 mL concentrate for solution and is packed in a carton with a blue colour code.
Pack size: 3 pre-filled syringes and 5 cannulas.
Korjuny 50 micrograms concentrate for solution for infusion:
The pre-filled syringe contains 0.5 mL concentrate for solution and is packed in a carton with a red colour code.
Pack size: 4 pre-filled syringes and 5 cannulas.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6. Special precautions for disposal and other handling
The pre-filled syringe is for single use only.
Material and equipment required for dilution and administration of Korjuny:
- sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection
- 50 mL polypropylene syringes
- cap for 50 mL polypropylene syringes
- polyethylene perfusion tubing with an inner diameter of 1 mm and a length of 150 cm
- polycarbonate infusion valves / Y connections
- polyurethane silicon-coated catheters
- precision perfusion pump
Dilution prior to administration:
Korjuny should be prepared by a healthcare professional using appropriate aseptic technique. The outer surface of the pre-filled syringe is not sterile.
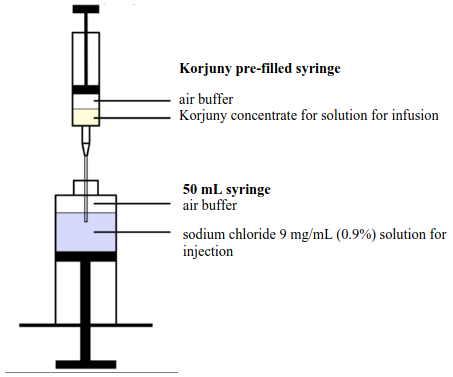
- The volume of sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection listed in Table 5 is extracted with a 50 mL syringe.
- An additional air buffer of at least 3 mL is included in the 50 mL syringe.
- The Korjuny pre-filled syringe(s) of the required strength listed in Table 5 below are visually inspected for any foreign particulates or discolouration.
- With the pre-filled syringe tip pointing up, the tip cap is gently removed. Do not twist off or rotate the cap.
- The enclosed cannula is attached to the pre-filled syringe and the cannula shield removed. A new cannula must be used for each syringe.
- The cannula is inserted through the 50 mL syringe opening so that the cannula is immersed in the sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection (Figure 2). Do not administer the Korjuny pre-filled syringe directly to a patient.
- The entire content of the pre-filled syringe is injected into the sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection.
- The plunger rod must not be drawn back to rinse the pre-filled syringe, to avoid contamination and to ensure that the correct volume is ejected.
- Based on Table 5, the previous steps are repeated to inject the required number of pre-filled syringes into the 50 mL syringe.
- The 50 mL syringe is closed with a cap and shaken gently to mix the solution.
- After removing the cap, any air bubbles are eliminated from the 50 mL syringe.
- The red peelable sticker, which is provided inside the carton lid, displaying the text “Diluted Korjuny. Intraperitoneal use only.” must be attached to the 50 mL syringe. This is a precautionary measure to ensure Korjuny is intraperitoneally infused only.
- The 50 mL syringe is inserted in the infusion pump.
Table 5. Number of pre-filled syringes and volumes required for preparation of Korjuny solution for intraperitoneal infusion:
| Infusion / Dose | Number of 10 micrograms pre-filled syringes | Number of 50 micrograms pre-filled syringes | Total volume of Korjuny concentrate for solution for infusion | Sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection | Final volume for administration |
| 1st infusion / 10 micrograms | 1 | --- | 0.1 mL | 10 mL | 10.1 mL |
| 2nd infusion / 20 micrograms | 2 | --- | 0.2 mL | 20 mL | 20.2 mL |
| 3rd infusion / 50 micrograms | --- | 1 | 0.5 mL | 49.5 mL | 50 mL |
| 4th infusion / 150 micrograms | --- | 3 | 1.5 mL | 48.5 mL | 50 mL |
Method of administration
The catheter for intraperitoneal administration is placed under ultrasound guidance by a doctor experienced in intraperitoneal administration. The catheter is used for ascites drainage, and administration of diluted Korjuny solution for infusion and sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection. It is recommended that the catheter remains in the abdominal cavity during the entire treatment period. It can be removed based on the judgement of the treating physician on the day after the last infusion.
Prior to each Korjuny administration, the ascites fluid must be drained until cessation of spontaneous flow or symptom relief (see section 4.4). Subsequently, prior to each Korjuny administration, 500 mL sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection shall be infused to support distribution of the antibody in the abdominal cavity.
Diluted Korjuny solution for infusion is intraperitoneally administered over an infusion time of at least 3 hours via a constant infusion pump system, as follows:
- The connected perfusion tubing equipment of the infusion pump is prefilled with the diluted Korjuny solution for infusion.
- The perfusion tubing is connected to the Y connection.
- Parallel to each Korjuny administration, 250 mL sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection is infused via an infusion valve / Y connection in the perfusion lead of the catheter.
- The pump speed is adjusted according to the volume to be administered and the scheduled infusion time of at least 3 hours.
- When the 50 mL syringe containing the diluted Korjuny solution for infusion is empty, it is replaced with a 50 mL syringe containing 20 mL sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection, to clear the dead volume in the perfusion lead (approximately 2 mL), under unchanged conditions. The remaining sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection can be discarded.
- The catheter is kept closed until the next infusion.
- The day after the last infusion, a drainage of ascites is performed until cessation of spontaneous flow. Subsequently, the catheter can be removed.
Disposal
No special requirements.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.