BESEMAX Tablet Ref.[50699] Active ingredients: Orphenadrine Paracetamol
Source: Health Products Regulatory Authority (ZA) Revision Year: 2022 Publisher: Adcock Ingram Limited, 1 New Road, Erand Gardens, Midrand, 1685, Private Bag X69, Bryanston, 2021 www.adcock.com 0860ADCOCK (232625)
4.1. Therapeutic indications
BESEMAX Tablet are indicated in generalised pain and the relief of muscle spasm associated with acute painful musculo-skeletal conditions.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Adults: 2 tablets 3 times a day.
DO NOT EXCEED THE RECOMMENDED DOSAGE.
4.9. Overdose
Prompt treatment is essential. In the event of an overdosage, consult a doctor immediately, or take the person directly to a hospital. A delay in starting treatment may mean that antidote is given too late to be effective. Evidence of liver damage is often delayed until after the time for effective treatment has lapsed.
Susceptibility to paracetamol toxicity is increased in patients who have taken repeated high doses (greater than 5-10 g/day) of paracetamol for several days, in chronic alcoholism, chronic liver disease, AIDS, malnutrition, and with the use of drugs that induce liver microsomal oxidation such as barbiturates, isoniazid, rifampicin, phenytoin and carbamazepine.
Symptoms of paracetamol overdosage in the first 24 hours include pallor, nausea, vomiting, anorexia and possibly abdominal pain. Mild symptoms during the first two days of acute poisoning, do not reflect the potential seriousness of the overdosage.
Liver damage may become apparent 12 to 48 hours, or later after ingestion, initially by elevation of the serum transaminase and lactic dehydrogenase activity, increased serum bilirubin concentration and prolongation of the prothrombin time. Liver damage may lead to encephalopathy, coma and death.
Acute renal failure with acute tubular necrosis may develop even in the absence of severe liver damage. Abnormalities of glucose metabolism and metabolic acidosis may occur. Cardiac arrhythmias have been reported.
Treatment for paracetamol overdosage
Although evidence is limited it is recommended that any adult person who has ingested 5-10 grams or more of paracetamol (or a child who has had more than 140 mg/kg) within the preceding four hours, should have the stomach emptied by lavage (emesis may be adequate for children) and a single dose of 50 g activated charcoal given via the lavage tube. Ingestion of amounts of paracetamol smaller than this may require treatment in patients susceptible to paracetamol poisoning (see above). In patients who are stuperose or comatose endotracheal intubation should precede gastric lavage in order to avoid aspiration.
N-acetylcysteine should be administered to all cases of suspected overdose as soon as possible preferably within eight hours of overdosage, although treatment up to 36 hours after ingestion may still be of benefit, especially if more than 150 mg/kg of paracetamol was taken. An initial dose of 150 mg/kg N-acetylcysteine in 200 ml dextrose injection given intravenously over 15 minutes, followed by an infusion of 50 mg/kg in 500 ml dextrose injection over the next four hours, and then 100 mg/kg in 1 000 ml dextrose injection over the next sixteen hours. The volume of intravenous fluid should be modified for children.
Although the oral formulation is not the treatment of choice, 140 mg/kg dissolved in water may be administered initially, followed by 70 mg/kg every four hours for seventeen doses.
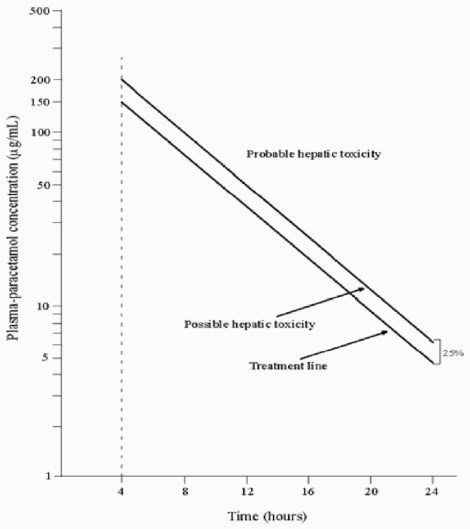
A plasma paracetamol level should be determined four hours after ingestion in all cases of suspected overdosage. Levels done before four hours may be misleading. Patients at risk of liver damage, and hence requiring continued treatment with N-acetylcysteine, can be identified according to their 4-hour plasma paracetamol level. The plasma paracetamol level can be plotted against time since ingestion in the nomogram below. The nomogram should be used only in relation to a single acute ingestion.
Those whose plasma paracetamol levels are above the “normal treatment line”, should continue N-acetylcysteine treatment with 100 mg/kg IV over sixteen hours repeatedly until recovery. Patients with increased susceptibility to liver damage as identified above, should continue treatment if concentrations are above the “high risk treatment line”. Prothrombin index correlates best with survival.
For overdose with an extended/modified release preparation the value of the nomogram is unknown. As there is no information on the plasma levels of paracetamol after an overdose of extended/modified release paracetamol preparations, all patients with suspected or known overdose with such preparations should receive N-acetylcysteine. Because of lack of data for extended/modified release formulations, a level below the “treatment line” of the nomogram may not exclude the possibility of toxicity.
Monitor all patients with significant ingestions for at least ninety six hours.
Figure 1. A semi-logarithmic plot of plasma-paracetamol concentration against hours after ingestion:
Orphenadrine citrate
Toxic doses cause tachycardia, rapid respiration, hyperpyrexia and central nervous system stimulation marked by restlessness, confusion, excitement, paranoid and psychotic reactions, hallucinations and delirium, and occasionally seizures or convulsions. A rash may appear on the face or upper trunk. In severe intoxication, central stimulation may give way to central nervous system depression, coma, circulatory and respiratory failure, and death.
Treatment is symptomatic and supportive. Institution of hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may be of some benefit if the serum concentration exceeds 4 mcg per 4 ml.
6.3. Shelf life
24 months.
6.4. Special precautions for storage
Store at or below 25ºC. Protect from light.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
6.5. Nature and contents of container
20,40 and 120 tablets packed in PVC/aluminium foil blister packs.
50 and 100 tablets packed in white polypropylene securitainers with white low-density polyethylene (LDPE) closures.
120 tablets packed in white high-density polyethylene (HDPE) containers with white LDPE closure or white HDPE screw-on closures.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.