GAMUNEX-C Solution for injection Ref.[11127] Active ingredients: Human normal immunoglobulin G
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2020
1. Indications and Usage
GAMUNEX-C is an immune globulin injection (human) 10% liquid that is indicated for the treatment of:
1.1 Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency (PI)
GAMUNEX-C is indicated for treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency in patients 2 years of age and older. This includes, but is not limited to, congenital agammaglobulinemia, common variable immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, and severe combined immunodeficiencies.(1-4)
1.2 Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
GAMUNEX-C is indicated for the treatment of adults and children with Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura to raise platelet counts to prevent bleeding or to allow a patient with ITP to undergo surgery.(5,6)
1.3 Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
GAMUNEX-C is indicated for the treatment of CIDP in adults to improve neuromuscular disability and impairment and for maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
2. Dosage and Administration
2.1 Preparation and Handling
- Visually inspect GAMUNEX-C for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if turbid.
- Do not freeze. Do not use solutions that have been frozen.
- Prior to use, allow the solution to reach ambient room temperature.
- If the packaging shows any signs of tampering, do not use the product and notify Grifols Therapeutics LLC immediately [1-800-520-2807].
- The GAMUNEX-C vial is for single use only. GAMUNEX-C contains no preservative. Use any vial that has been entered promptly. Discard partially used vials. Do not store after entry into vial.
- Infuse GAMUNEX-C using a separate line by itself, without mixing with other intravenous fluids or medications the subject might be receiving.
The GAMUNEX-C infusion line can be flushed with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W) or 0.9% sodium chloride for injection.
- If dilution is required, GAMUNEX-C may be diluted with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W). Do not dilute with saline.
- Content of vials may be pooled under aseptic conditions into sterile infusion bags and infused within 8 hours after pooling.
- Avoid simultaneous administration of GAMUNEX-C and Heparin through a single lumen delivery device due to GAMUNEX-C, Heparin incompatibilities. Flush Heparin Lock (Hep-Lock) through which GAMUNEX-C was administered with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W) or 0.9% sodium chloride for injection, and do not flush with Heparin. See table below.
| Additional Solutions | Dilution | Line Flush | Delivery Device Flush |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5% Dextrose in water | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 0.9% Sodium Chloride | No | Yes | Yes |
| Heparin | No | No | No |
- Do not mix with immune globulin intravenous (IGIV) products from other manufacturers.
- Do not use after expiration date.
2.2 PI
As there are significant differences in the half-life of IgG among patients with primary humoral immunodeficiencies, the ideal frequency and amount of immunoglobulin therapy may vary from patient to patient. The proper amount can be determined by monitoring clinical response.
Intravenous (IV)
The dose of GAMUNEX-C for patients with PI is 300 mg/kg to 600 mg/kg body weight (3 mL/kg to 6 mL/kg) administered every 3 to 4 weeks. The dosage may be adjusted over time to achieve the desired trough levels and clinical responses.
The recommended initial infusion rate is 1 mg/kg/min (0.01 mL/kg/min). If the infusion is well-tolerated, the rate may be gradually increased to a maximum of 8 mg/kg/min (0.08 mL/kg/min). For patients judged to be at risk for renal dysfunction or thrombosis, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum infusion rate practicable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2,5.4)].
If a patient routinely receives a dose of less than 400 mg/kg of GAMUNEX-C every 3 to 4 weeks (less than 4 mL/kg), and is at risk of measles exposure (i.e., traveling to a measles endemic area), administer a dose of at least 400 mg/kg (4 mL/kg) just prior to the expected measles exposure. If a patient has been exposed to measles, a dose of 400 mg/kg (4 mL/kg) should be administered as soon as possible after exposure.
Subcutaneous (SC)
The dose should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical response to GAMUNEX-C therapy and serum IgG trough levels. Begin treatment with GAMUNEX-C one week after the patient’s last IGIV infusion. See below under “Initial Weekly Dose”. Prior to switching treatment from IGIV to GAMUNEX-C, obtain the patient’s serum IgG trough level to guide subsequent dose adjustments. See below under “Dose Adjustment”.
Establish the initial weekly dose of GAMUNEX-C by converting the monthly IGIV dose into a weekly equivalent and increasing it using a dose adjustment factor. The goal is to achieve a systemic serum IgG exposure (Area Under the Concentration-Time Curve [AUC]) not inferior to that of the previous IGIV treatment. If the patient has not been previously treated with IV GAMUNEX-C, convert the monthly IGIV dose (in grams) by multiplying by 1.37, then dividing this dose into weekly doses based on the patient’s previous IGIV treatment interval. Monitor the patient’s clinical response, and adjust dose accordingly.
Initial Weekly Dose:
To calculate the initial weekly dose of subcutaneous administration of GAMUNEX-C, multiply the previous IGIV dose in grams by the dose adjustment factor of 1.37; then divide this by the number of weeks between doses during the patient’s IGIV treatment (i.e., 3 or 4).
Initial SC dose (in grams) = 1.37 × previous IGIV dose (in grams) / Number of weeks between IGIV doses
To convert the GAMUNEX-C dose (in grams) to milliliters (mL), multiply the calculated Initial SC dose (in grams) by 10.
Dose Adjustment:
Over time, the dose may need to be adjusted to achieve the desired clinical response and serum IgG trough level. To determine if a dose adjustment may be considered, measure the patient’s serum IgG trough level on IGIV and as early as 5 weeks after switching from IGIV to subcutaneous. The target serum IgG trough level on weekly SC treatment is projected to be the last IGIV trough level plus 340 mg/dL. To determine if further dose adjustments are necessary, monitor the patient’s IgG trough level every 2 to 3 months.
To adjust the dose based on trough levels, calculate the difference (in mg/dL) of the patient’s serum IgG trough level from the target IgG trough level (the last IGIV trough level + 340 mg/dL). Then find this difference in Table 1 and the corresponding amount (in mL) by which to increase or decrease the weekly dose based on the patient’s body weight. However, the patient’s clinical response should be the primary consideration in dose adjustment.
Table 1. Adjustment (±mL) of the Weekly Subcutaneous Dose Based on the Difference (±mg/dL) From the Target Serum IgG Trough Level:
| Difference From Target IgG Trough Level (mg/dL) | Body Weight (kg) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | |
| Dose Adjustment (mL per Week)* | |||||||||||||
| 50 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 100 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 20 |
| 150 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 23 | 25 | 28 | 30 |
| 200 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 17 | 20 | 23 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 37 | 40 |
| 250 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 13 | 17 | 21 | 25 | 29 | 33 | 38 | 42 | 46 | 50 |
| 300 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 |
| 350 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 23 | 29 | 35 | 41 | 47 | 53 | 58 | 64 | 70 |
| 400 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 20 | 27 | 33 | 40 | 47 | 53 | 60 | 67 | 73 | 80 |
| 450 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 23 | 30 | 38 | 45 | 53 | 60 | 68 | 75 | 83 | 90 |
| 500 | 8 | 13 | 17 | 25 | 33 | 42 | 50 | 58 | 67 | 75 | 83 | 92 | 100 |
* Dose adjustment in mL is based on the slope of the serum IgG trough level response to subcutaneous administration of GAMUNEX-C dose increments (about 6.0 mg/dL per increment of 1 mg/kg per week).
For example, if a patient with a body weight of 70 kg has an actual IgG trough level of 900 mg/dL and the target level is 1,000 mg/dL, this results in a difference of 100 mg/dL. Therefore, increase the weekly dose of subcutaneous dose by 12 mL.
Monitor the patient’s clinical response, and repeat the dose adjustment as needed.
Dosage requirements for patients switching to GAMUNEX-C from another Immune Globulin Subcutaneous (IGSC) product have not been studied. If a patient on GAMUNEX-C does not maintain an adequate clinical response or a serum IgG trough level equivalent to that of the previous IGSC treatment, adjust the dose accordingly. For such patients, Table 1 also provides guidance for dose adjustment to achieve a desired IGSC trough level.
2.3 ITP
DO NOT ADMINISTER SUBCUTANEOUSLY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
GAMUNEX-C may be administered at a total dose of 2 g/kg, divided in two doses of 1 g/kg (10 mL/kg) given on two consecutive days or into five doses of 0.4 g/kg (4 mL/kg) given on five consecutive days. If after administration of the first of two daily 1 g/kg (10 mL/kg) doses, an adequate increase in the platelet count is observed at 24 hours, the second dose of 1g/kg (10 mL/kg) body weight may be withheld.
The high dose regimen (1 g/kg × 1-2 days) is not recommended for individuals with expanded fluid volumes or where fluid volume may be a concern [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Clinical Studies (14)].
The recommended initial infusion rate is 1 mg/kg/min (0.01 mL/kg/min). If the infusion is well-tolerated, the rate may be gradually increased to a maximum of 8 mg/kg/min (0.08 mL/kg/min). For patients judged to be at risk for renal dysfunction or thrombosis, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum infusion rate practicable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2,5.4)].
2.4 CIDP
GAMUNEX-C may be initially administered as a total loading dose of 2 g/kg (20 mL/kg) given in divided doses over two to four consecutive days. GAMUNEX-C may be administered as a maintenance infusion of 1 g/kg (10 mL/kg) administered over 1 day or divided into two doses of 0.5 g/kg (5 mL/kg) given on two consecutive days, every 3 weeks. Not all patients may require continued maintenance therapy beyond the initial 6 months of therapy in order to maintain their therapeutic response.
The recommended initial infusion rate is 2 mg/kg/min (0.02 mL/kg/min). If the infusion is well tolerated, the rate may be gradually increased to a maximum of 8 mg/kg/min (0.08 mL/kg/min). For patients judged to be at risk for renal dysfunction or thrombosis, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum infusion rate practicable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2,5.4)].
2.5 Administration
Administer intravenously for PI, ITP and CIDP.
GAMUNEX-C may also be administered subcutaneously for the treatment of PI.
- Administer GAMUNEX-C at room temperature.
- Inspect GAMUNEX-C visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever the solution and container permit.
- Do not use if turbid and/or if discoloration is observed.
Intravenous
- Use only 18 gauge needles to penetrate the stopper for dispensing product from the 10 mL vial.
- Use 16 gauge needles or dispensing pins only with 25 mL vial sizes and larger.
- Insert needles or dispensing pins only once and be within the stopper area delineated by the raised ring.
- Penetrate the stopper perpendicular to the plane of the stopper within the ring.
| GAMUNEX-C vial size | Gauge of needle to penetrate stopper |
|---|---|
| 10 mL | 18 gauge |
| 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 mL | 16 gauge |
- Use promptly any vial that has been opened.
- Discard partially used vials.
- If dilution is required, GAMUNEX-C may be diluted with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W). Do not dilute with saline. Infuse GAMUNEX-C using a separate line by itself, without mixing with other intravenous fluids or medications the subject might be receiving. The GAMUNEX-C infusion line can be flushed with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W) or 0.9% sodium chloride for injection.
Subcutaneous for PI Only
Instructions for Administration:
- Prior to use, allow the solution to reach ambient room temperature.
- DO NOT SHAKE.
- Do not use if the solution is cloudy or has particulates.
- Check the product expiration date on the vial. Do not use beyond the expiration date.
- Use aseptic technique when preparing and administering GAMUNEX-C for injection.
- Remove the protective cap from the vial to expose the central portion of the stopper. If the packaging shows any sign of tampering, do not use the product and notify Grifols Therapeutics LLC immediately [1-800-520-2807].
- Wipe the stopper with alcohol and allow to dry.
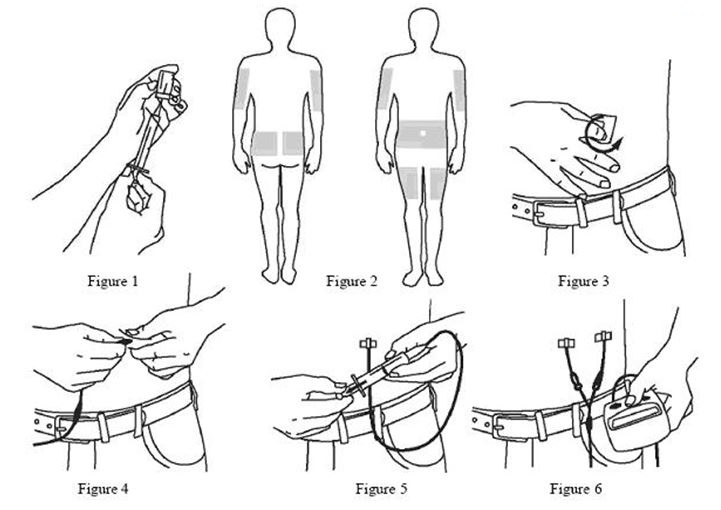
- Using a sterile syringe and needle, prepare to withdraw GAMUNEX-C by first injecting air into the vial that is equivalent to the amount of GAMUNEX-C to be withdrawn. Then withdraw the desired volume of GAMUNEX-C. If multiple vials are required to achieve the desired dose, repeat this step. (Figure 1)
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for filling the pump reservoir and preparing the pump, administration tubing and Y-site connection tubing, if needed. Be sure to prime the administration tubing to ensure that no air is left in the tubing or needle by filling the tubing/needle with GAMUNEX-C.
- Select the number and location of injection sites. (Figure 2)
- Cleanse the injection site(s) with antiseptic solution using a circular motion working from the center of the site and moving to the outside. Sites should be clean, dry, and at least two inches apart. (Figure 3)
- Grasp the skin between two fingers and insert the needle into the subcutaneous tissue. (Figure 4)
- After inserting each needle, make sure that a blood vessel has not been accidentally entered. Attach a sterile syringe to the end of the primed administration tubing, pull back on the plunger, and if you see blood, remove and discard the needle and administration tubing. (Figure 5)
- Repeat priming and needle insertion steps using a new needle, administration tubing and a new infusion site. Secure the needle in place by applying sterile gauze or transparent dressing over the site.
- If using multiple, simultaneous injection sites, use Y-site connection tubing and secure to the administration tubing.
- Infuse GAMUNEX-C following the manufacturer’s instructions for the pump. (Figure 6)
Rate of Administration
Intravenous
Following initial infusion (see table below), the infusion rate may be gradually increased to a maximum of 0.08 mL/kg per minute (8 mg/kg per minute) as tolerated.
| Indication | Initial Infusion Rate (first 30 minutes) | Maximum Infusion Rate (if tolerated) |
|---|---|---|
| PI | 1 mg/kg/min | 8 mg/kg/min |
| ITP | 1 mg/kg/min | 8 mg/kg/min |
| CIDP | 2 mg/kg/min | 8 mg/kg/min |
Monitor patient vital signs throughout the infusion. Slow or stop infusion if adverse reactions occur. If symptoms subside promptly, the infusion may be resumed at a lower rate that is comfortable for the patient.
Certain severe adverse drug reactions may be related to the rate of infusion. Slowing or stopping the infusion usually allows the symptoms to disappear promptly.
Ensure that patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency are not volume depleted. For patients at risk of renal dysfunction or thrombosis, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum infusion rate practicable and discontinue GAMUNEX-C if renal function deteriorates.
Subcutaneous for PI Only
For PI, it is recommended that GAMUNEX-C is infused at a rate of 20 mL per hour per infusion site for adults, and up to 8 infusion sites may be used (most patients used 4 infusion sites). Children and adolescents weighing ≥25 kg should start out at a slower infusion rate of 15 mL/hour/infusion site and increase their infusion rate up to 20 mL/hour/infusion site. For children and adolescents weighing <25 kg, a rate of 10 mL/hour/infusion site is recommended. In children up to 6 infusion sites simultaneously may be used. For patients of all ages ensure that the infusion sites are at least 2 inches (5 cm) apart.
10. Overdosage
With intravenous administration, overdose of GAMUNEX-C may lead to fluid overload and hyperviscosity. Patients at risk of complications of fluid overload and hyperviscosity include elderly patients and those with cardiac renal impairment.
16.2. Storage and Handling
- DO NOT FREEZE
- Keep the vial in the carton to protect from light.
- GAMUNEX-C may be stored for 36 months at 2-8°C (36-46°F) from the date of manufacture, AND product may be stored at temperatures not to exceed 25°C (77°F) for up to 6 months anytime during the 36 month shelf life, after which the product must be immediately used or discarded.
- Do not use after expiration date.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.