GYNAZOLE-1 Cream Ref.[49690] Active ingredients:
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2021
2. Clinical Pharmacology
Following vaginal administration of butoconazole nitrate vaginal cream, 2% to 3 women, 1.7% (range 1.3-2.2%) of the dose was absorbed on average. Peak plasma levels (13.6-18.6 ng radioequivalents/mL of plasma) of the drug and its metabolites are attained between 12 and 24 hours after vaginal administration.
Microbiology
The exact mechanism of the antifungal action of butoconazole nitrate is unknown; however, it is presumed to function as other imidazole derivatives via inhibition of steroid synthesis. Imidazoles generally inhibit the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol, resulting in a change in fungal cell membrane lipid composition. This structural change alters cell permeability and, ultimately, results in the osmotic disruption or growth inhibition of the fungal cell.
Butoconazole nitrate is an imidazole derivative that has fungicidal activity in vitro against Candida spp. and has been demonstrated to be clinically effective against vaginal infections due to Candida albicans. Candida albicans has been identified as the predominant species responsible for vulvovaginal candidiasis.
6.6. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of this drug.
Mutagenicity
Butoconazole nitrate was not mutagenic when tested in the Ames bacterial test, yeast, chromosomal aberration assay in CHO cells, CHO/HGPRT point mutation assay, mouse micronucleus, and rat dominant lethal assays.
Impairment of Fertility
No impairment of fertility was seen in rabbits or rats administered butoconazole nitrate in oral doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (5 times the human dose based on mg/m2) or 100 mg/kg/day (10 times the human dose based on mg/m2), respectively.
13. Clinical Studies
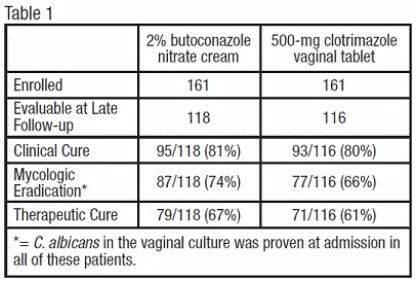
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis: Two studies were conducted that compared 2% butoconazole nitrate cream with clotrimazole tablets. There were 322 enrolled patients, 161 received 2.0% butoconazole vaginal cream and 161 patients inserted the 500-mg clotrimazole vaginal tablet. At the second follow-up visit (30 days post-therapy), 118 patients in the butoconzole group and 116 in the clotrimazole group were evaluable for efficacy analysis, respectively. All of these patients had infection caused by Candida albicans.
The efficacy of the study drugs was assessed by evaluating clinical, mycologic and therapeutic cure rates, which are summarized in Table 1.
The therapeutic cure was defined as complete resolution of signs and symptoms of vaginal candidiasis (clinical cure) along with a negative KOH examination and negative culture for Candida spp. (microbiologic eradication) at the long term follow-up (30 days). The therapeutic cure rate was 67% in the butoconazole group and 61% in the clotrimazole group.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.