NURTEC ODT Orally disintegrating tablet Ref.[10188] Active ingredients: Rimegepant
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2020
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Rimegepant is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist.
12.2. Pharmacodynamics
The relationship between pharmacodynamic activity and the mechanism(s) by which rimegepant exerts its clinical effects is unknown.
No clinically relevant differences in resting blood pressure were observed when rimegepant was concomitantly administered with sumatriptan (12 mg subcutaneous, given as two 6 mg doses separated by one hour) compared with sumatriptan alone to healthy volunteers.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a single dose 4 times the recommended dose, rimegepant does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3. Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration of NURTEC ODT, rimegepant is absorbed with the maximum concentration at 1.5 hours. The absolute oral bioavailability of rimegepant is approximately 64%.
Effects of Food
Following administration of NURTEC ODT under fed condition with a high-fat meal, Tmax was delayed by 1 hour and resulted in a 42 to 53% reduction in Cmax and a 32 to 38% reduction in AUC. NURTEC ODT was administered without regard to food in clinical safety and efficacy studies. The impact of the reduction in rimegepant exposure because of administration with food on its efficacy is unknown.
Distribution
The steady state volume of distribution of rimegepant is 120 L. Plasma protein binding of rimegepant is approximately 96%.
Elimination
Metabolism
Rimegepant is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9.
Rimegepant is primarily eliminated in unchanged form (~77% of the dose) with no major metabolites (i.e., >10%) detected in plasma.
Excretion
The elimination half-life of rimegepant is approximately 11 hours in healthy subjects. Following oral administration of [14C]-rimegepant to healthy male subjects, 78% of the total radioactivity was recovered in feces and 24% in urine. Unchanged rimegepant is the major single component in excreted feces (42%) and urine (51%).
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
In a dedicated clinical study comparing the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant in subjects with mild (estimated creatinine clearance [CLcr] 60-89 mL/min), moderate (CLcr 30-59 mL/min), and severe (CLcr 15-29 mL/min) renal impairment to that with normal subjects (healthy matched control), the exposure of rimegepant following single 75 mg dose was approximately 40% higher in subjects with moderate renal impairment. However, there was no clinically meaningful difference in the exposure of rimegepant in subjects with severe renal impairment compared to subjects with normal renal function (CLcr ≥90mL/min). NURTEC ODT has not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease (CLcr <15 mL/min) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Hepatic Impairment
In a dedicated clinical study comparing the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment to that with normal subjects (healthy matched control), the exposure of rimegepant (Cmax and AUC) following single 75 mg dose was approximately 2-fold higher in subjects with severe impairment (Child-Pugh class C). There were no clinically meaningful differences in the exposure of rimegepant in subjects with mild (Child-Pugh class A) and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B) compared to subjects with normal hepatic function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Other Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant were observed based on age, sex, race/ethnicity, body weight, or CYP2C9 genotype [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)].
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies
Enzymes:
Rimegepant is a substrate of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 (see In Vivo Studies). Rimegepant is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or UGT1A1 at clinically relevant concentrations. However, rimegepant is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4 with time-dependent inhibition. Rimegepant is not an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Transporters:
Rimegepant is a substrate of P-gp and BCRP. Concomitant administration of inhibitors of P-gp or BCRP may increase the exposure of rimegepant [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. No dedicated drug interaction study was conducted to assess their effects on the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant.
Rimegepant is not a substrate of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3. Considering its low renal clearance, rimegepant was not evaluated as a substrate of the OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, or MATE2‑K.
Rimegepant is not an inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP, OAT1, or MATE2-K at clinically relevant concentrations. It is a weak inhibitor of OATP1B1 and OAT3. Rimegepant is an inhibitor of OATP1B3, OCT2, and MATE1. No clinical drug interactions are expected for NURTEC ODT with these transporters at clinically relevant concentrations.
In Vivo Studies
CYP3A4 Inhibitors:
In a dedicated drug interaction study, concomitant administration of 75 mg rimegepant (single dose) with itraconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, at steady state resulted in increased exposures of rimegepant (AUC by 4-fold and Cmax by ~1.5-fold) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. No dedicated drug interaction study was conducted to assess the effect of concomitant administration of a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4 on the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant. The concomitant administration of rimegepant with a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4 may increase rimegepant exposures (AUC) by less than 2-fold [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Concomitant administration of rimegepant with a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4 is not expected to have a clinically significant impact on rimegepant exposures.
CYP3A Inducers:
In a dedicated drug interaction study, concomitant administration of 75 mg rimegepant (single dose) with rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, at steady state resulted in decreased exposures of rimegepant (AUC by 80% and Cmax by 64%), which may lead to loss of efficacy [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. No dedicated drug interaction study was conducted to assess the effect of concomitant administration of a moderate or weak inducer of CYP3A4 on the pharmacokinetics of rimegepant. Since rimegepant is a moderately sensitive substrate for CYP3A4, drugs that are moderate inducers of CYP3A4 can also cause significant reduction in rimegepant exposure resulting in loss of efficacy [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Clinically significant interaction is not expected with concomitant administration of weak inducers of CYP3A4 and rimegepant.
CYP2C9 Inhibitors:
In a dedicated drug interaction study, concomitant administration of 75 mg rimegepant (single dose) with fluconazole, a combined moderate CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 inhibitor, resulted in increased exposures of rimegepant (AUC by 1.8-fold) with no relevant effect on Cmax. Rimegepant is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9. Increase in the exposure of rimegepant can be attributed to combined inhibition of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 with fluconazole administration suggesting a minor contribution from CYP2C9. Thus, CYP2C9 inhibition alone is not expected to significantly affect rimegepant exposures.
Other Drugs:
No significant pharmacokinetic interactions were observed when rimegepant was concomitantly administered with oral contraceptives (norelgestromin, ethinyl estradiol), midazolam (a sensitive CY3A4 substrate), or sumatriptan [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
12.5. Pharmacogenomics
CYP2C9 activity is reduced in individuals with genetic variants such as the CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 alleles. Rimegepant Cmax and AUC0-inf were similar in CYP2C9 intermediate metabolizers (i.e., *1/*2, *2/*2, *1/*3, n=43) as compared to normal metabolizers (i.e., *1/*1, N=72). Adequate PK data are not available from CYP2C9 poor metabolizers (i.e., *2/*3). Since the contribution of CYP2C9 to rimegepant metabolism is considered minor, CYP2C9 polymorphism is not expected to significantly affect its exposure.
13.1. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Oral administration of rimegepant to Tg.rasH2 mice (0, 10, 100, or 300 mg/k/day) for 26 weeks and to rats (0, 5, 20, or 45 mg/kg/day) for 91-100 weeks resulted in no evidence of drug-induced tumors in either species. In rats, the plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested (45 mg/kg/day) was approximately 30 times that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 75 mg/day.
Mutagenesis
Rimegepant was negative in in vitro (bacterial reverse-mutation, chromosomal aberration in Chinese hamster ovary cells) and in vivo (rat micronucleus) assays.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of rimegepant (0, 30, 60, or 150 mg/kg/day) to male and female rats prior to and during mating and continuing in females to gestation day (GD) 7 resulted in uterine atrophy at all doses and reduced fertility at the highest dose tested. In a second fertility study testing lower doses (0, 5, 15, or 25 mg/kg/day), no adverse effects on fertility, uterine histopathology, or early embryonic development were observed. The no-effect dose for impairment of fertility and early embryonic development in rats (25 mg/kg/day) was associated with plasma drug exposures (AUC) approximately 15 times that in humans at the MRHD.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of NURTEC ODT for the acute treatment of migraine with and without aura in adults was demonstrated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial: Study 1 (NCT03461757). The study randomized patients to 75 mg of NURTEC ODT (N=732) or placebo (N=734). Patients were instructed to treat a migraine of moderate to severe headache pain intensity. Rescue medication (i.e., NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and/or an antiemetic) was allowed 2 hours after the initial treatment. Other forms of rescue medication such as triptans were not allowed within 48 hours of initial treatment. Approximately 14% of patients were taking preventive medications for migraine at baseline. None of the patients in Study 1 were on concomitant preventive medication that act on the CGRP pathway.
The primary efficacy analyses were conducted in patients who treated a migraine with moderate to severe pain. NURTEC ODT 75 mg demonstrated an effect on pain freedom and most bothersome symptom (MBS) freedom at two hours after dosing, compared to placebo. Pain freedom was defined as a reduction of moderate or severe headache pain to no headache pain, and MBS freedom was defined as the absence of the self-identified MBS (i.e., photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea). Among patients who selected an MBS, the most commonly selected symptom was photophobia (54%), followed by nausea (28%), and phonophobia (15%).
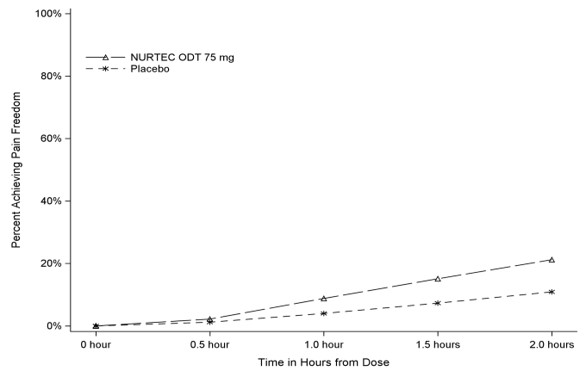
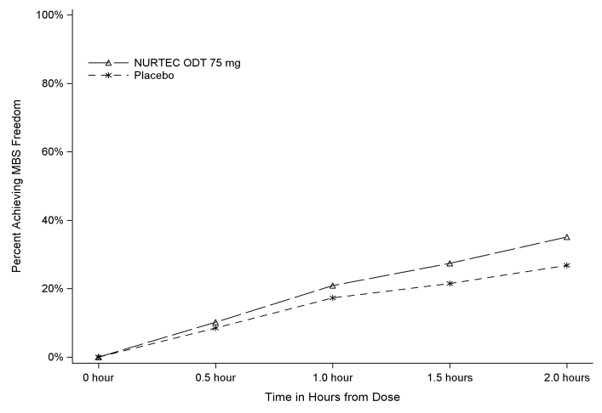
In Study 1, the percentage of patients achieving headache pain freedom and MBS freedom two hours after a single dose was statistically significantly greater in patients who received NURTEC ODT compared to those who received placebo (Table 1).
Table 1. Migraine Efficacy Endpoints for Study 1:
| Study 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| NURTEC ODT 75 mg | Placebo | |
| Pain Free at 2 hours | ||
| n/N* | 142/669 | 74/682 |
| % Responders | 21.2 | 10.9 |
| Difference from placebo (%) | 10.3 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | |
| MBS Free at 2 hours | ||
| n/N* | 235/669 | 183/682 |
| % Responders | 35.1 | 26.8 |
| Difference from placebo (%) | 8.3 | |
| p-value | 0.001 | |
* n=number of responders/N=number of patients in that treatment group
Figure 1 presents the percentage of patients achieving migraine pain freedom within 2 hours following treatment in Study 1.
Figure 1. Percentage of Patients Achieving Pain Freedom within 2 Hours in Study 1:
Figure 2 presents the percentage of patients achieving MBS freedom within 2 hours in Study 1.
Figure 2. Percentage of Patients Achieving MBS Freedom within 2 Hours in Study 1:
Table 2. Additional Migraine Efficacy Endpoints in Study 1:
| Study 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| NURTEC ODT 75 mg | >Placebo | |
| Pain Relief at 2 hours | ||
| n/N* | 397/669 | 295/682 |
| % Responders | 59.3 | 43.3 |
| Difference from placebo | 16.1 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | |
| Sustained Pain Freedom 2-48 hours | ||
| n/N* | 90/669 | 37/682 |
| % Responders | 13.5 | 5.4 |
| Difference from placebo | 8.0 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | |
| Use of Rescue Medication within 24 hours** | ||
| n/N* | 95/669 | 199/682 |
| % Responders | 14.2 | 29.2 |
| Difference from placebo | -15.0 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | |
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Normal Function at 2 hours | ||
| n/N* | 255/669 | 176/682 |
| % Responders | 38.1 | 25.8 |
| Difference from placebo | 12.3 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | |
* n=number of responders/N=number of patients in that treatment group
** This analysis includes only the use of NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or antiemetics, within 24 hours post-dose; the use of triptans, or other acute migraine medication, was not allowed.
The incidence of photophobia and phonophobia was reduced following administration of NURTEC ODT 75 mg as compared to placebo.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.