RYSTIGGO Solution for injection Ref.[107277] Active ingredients: Rozanolixizumab
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2023
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Rozanolixizumab-noli is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), resulting in the reduction of circulating IgG.
12.2. Pharmacodynamics
In Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)], the pharmacological effect of rozanolixizumab-noli was assessed by measuring the decrease in serum IgG levels and AChR and MuSK autoantibody levels. In patients testing positive for AChR and MuSK autoantibodies who were treated with RYSTIGGO, there was a reduction in total IgG levels relative to baseline. Decreases in AChR autoantibody and MuSK autoantibody levels followed a similar pattern.
12.3. Pharmacokinetics
Rozanolixizumab-noli exhibited nonlinear pharmacokinetics. Rozanolixizumab-noli exposure increased in a greater than dose-proportional manner over a dose range from 1 mg/kg to 20 mg/kg (two times the maximum recommended dose) following subcutaneous administration.
Absorption
Following subcutaneous administration of rozanolixizumab-noli, peak plasma levels were achieved after approximately 2 days in healthy subjects.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of rozanolixizumab-noli is 6.6 L.
Elimination
Metabolism
Rozanolixizumab-noli is expected to be degraded by proteolytic enzymes into small peptides and amino acids.
Excretion
The apparent clearance for the rozanolixizumab-noli is 0.89 L/day.
Specific Populations
Age, Sex, and Race
The pharmacokinetics of rozanolixizumab-noli were not affected by age, sex, or race based on a population pharmacokinetics analysis.
Patients with Renal Impairment
No dedicated pharmacokinetic study has been conducted in patients with renal impairment. Renal impairment is not expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of rozanolixizumab-noli. Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, which included participants with mild to moderate renal impairment, renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] 38–161 mL/min/1.73 m2) had no clinically significant effect on rozanolixizumab-noli apparent clearance. No dose adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dedicated pharmacokinetic study has been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment. Hepatic impairment is not expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of rozanolixizumab-noli.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical drug interaction studies have not been performed with rozanolixizumab-noli.
P450 Enzymes
Rozanolixizumab-noli is not metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Interactions with concomitant medications that are substrates, inducers, or inhibitors of cytochrome P450 enzymes are unlikely.
Drug Interactions with Other Drugs or Biological Products
Rozanolixizumab-noli may decrease concentrations of compounds that bind to the human FcRn [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
13.1. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Studies to assess the carcinogenic potential of rozanolixizumab-noli have not been conducted.
Studies to assess the genotoxic potential of rozanolixizumab-noli have not been conducted.
Impairment of Fertility
Subcutaneous administration of rozanolixizumab-noli (0 or 150 mg/kg) every 3 days for 26 weeks to sexually mature cynomolgus monkeys resulted in no adverse effects on sperm parameters (count, motility, or morphology) or estrus cyclicity. The dose tested in monkeys is 30 times the maximum recommended human dose of approximately 10 mg/kg, on a mg/kg/week basis.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of RYSTIGGO for the treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) in adults who are anti-AChR antibody positive or anti-MuSK antibody positive was established in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (Study 1; NCT03971422). The study included a 4-week screening period and a 6-week treatment period followed by 8 weeks of observation. During the treatment period, RYSTIGGO or placebo were administered subcutaneously once a week for six weeks.
Study 1 enrolled patients who met the following criteria:
- Presence of autoantibodies against AChR or MuSK
- Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America (MGFA) Clinical Classification Class II to IVa
- Myasthenia Gravis-Activities of Daily Living (MG-ADL) total score of at least 3 (with at least 3 points from non-ocular symptoms)
- On stable dose of MG therapy prior to screening that included acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors, steroids, or non-steroidal immunosuppressive therapies (NSISTs), either in combination or alone
- Serum IgG levels of at least 5.5 g/L
In Study 1, a total of 200 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to receive weight-tiered doses of RYSTIGGO (n=133), equivalent to ≈7 mg/kg (n=66) or ≈10 mg/kg (n=67), or placebo (n=67). Baseline characteristics were similar between treatment groups. Patients had a median age of 52 years at baseline (range: 18 to 89 years) and a median time since diagnosis of 6 years. Sixty-one percent of patients were female, 68% were White, 11% were Asian, 3% were Black or African American, 1% were American Indian or Alaska Native, and 7% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Median MG-ADL total score was 8, and the median Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis (QMG) total score was 15. The majority of patients, 89.5% (n=179) were positive for AChR antibodies and 10.5% (n=21) were positive for MuSK antibodies.
At baseline in each group, over 83% of patients received AChE inhibitors, over 56% of patients received steroids, and approximately 50% received NSISTs, at stable doses.
Patients were treated with RYSTIGGO via subcutaneous infusion once per week for a period of 6 weeks [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)], followed by an observation period of up to 8 weeks.
The efficacy of RYSTIGGO was measured using the MG-ADL scale, which assesses the impact of gMG on daily functions of 8 signs or symptoms that are typically affected in gMG. Each item is assessed on a 4-point scale where a score of 0 represents normal function and a score of 3 represents loss of ability to perform that function. A total score ranges from 0 to 24, with the higher scores indicating more impairment.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the comparison of the change from baseline between treatment groups in the MG-ADL total score at day 43. A statistically significant difference favoring RYSTIGGO was observed in the MG-ADL total score change from baseline [-3.4 points in RYSTIGGO-treated group at either dose vs -0.8 points in the placebo-treated group (p<0.001)].
The secondary endpoint was the change between treatment groups from baseline to day 43 in the QMG. The QMG is a 13-item categorical grading system that assesses muscle weakness. Each item is assessed on a 4-point scale where a score of 0 represents no weakness and a score of 3 represents severe weakness. A total possible score ranges from 0 to 39, where higher scores indicate more severe impairment.
A statistically significant difference favoring RYSTIGGO was observed in the QMG total score change from baseline [-5.4 points and -6.7 points in RYSTIGGO-treated group at ≈7 mg/kg and ≈10 mg/kg dose level, respectively, vs -1.9 points in the placebo-treated group (p<0.001)].
The results are presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Change from Baseline to Day 43 in MG-ADL and QMG Total Score in Adult Patients who are Anti-AChR or Anti-MuSK Antibody Positive (Study 1):
| Efficacy Endpoints | RYSTIGGO ≈7mg/kg N = 66 | RYSTIGGO ≈10mg/kg N = 67 | Placebo N = 67 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MG-ADL Total Score | |||
| LS Mean (SE) | -3.4 (0.5) | -3.4 (0.5) | -0.8 (0.5) |
| Difference from placebo (95% CI) | -2.6 (-4.1, -1.2) | -2.6 (-4.0, -1.2) | - |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | - |
| QMG Total Score | |||
| LS Mean (SE) | -5.4 (0.7) | -6.7 (0.7) | -1.9 (0.7) |
| Difference from placebo (95% CI) | -3.5 (-5.6, -1.6) | -4.8 (-6.8, -2.9) | - |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | - |
Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; MG-ADL, myasthenia gravis activities of daily living scale; QMG, quantitative myasthenia gravis; LS = least square; SE = standard error.
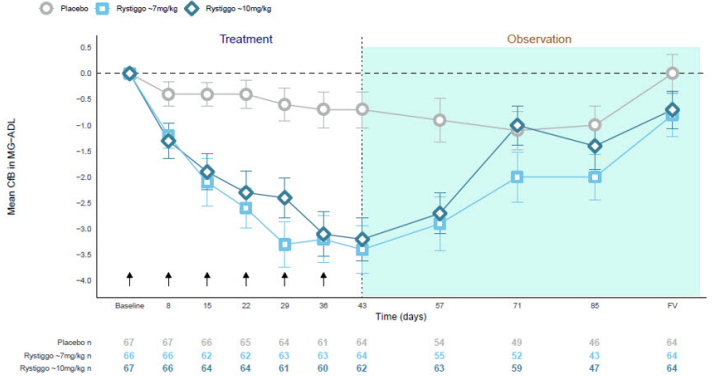
Figure 1 shows the mean change from baseline in MG-ADL score at Day 43 in Study 1.
Figure 1. Observed Mean Change from Baseline to Day 43 in MG-ADL Score:
CfB=Change from Baseline; FV=Final Visit; MG−ADL=Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living.
NOTE: Error bars represent +/− standard error; arrows indicate timepoints at which treatment was given.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.