TRUQAP Film-coated tablet Ref.[107254] Active ingredients: Capivasertib
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2023
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Capivasertib is an inhibitor of all 3 isoforms of serine/threonine kinase AKT (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) and inhibits phosphorylation of downstream AKT substrates. AKT activation in tumors is a result of activation of upstream signaling pathways, mutations in AKT1, loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) function and mutations in the catalytic subunit alpha of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PIK3CA).
In vitro, capivasertib reduced growth of breast cancer cell lines including those with relevant PIK3CA or AKT1 mutations or PTEN alteration. In vivo, capivasertib alone and in combination with fulvestrant inhibited tumor growth of mouse xenograft models including estrogen receptor positive breast cancer models with alterations in PIK3CA, AKT1, and PTEN.
12.2. Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response Relationships
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the effectiveness of capivasertib have not been fully characterized. Exposure-response relationships were observed for diarrhea (CTCAE Grade 2 to 4), rash (CTCAE Grade 2 to 4) and hyperglycemia (CTCAE Grades 3 or 4) at doses of 80 to 800 mg (0.2 to 2 times the approved recommended dosage).
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At the recommended TRUQAP dose, a mean increase in the QTc interval >20 ms was not observed.
12.3. Pharmacokinetics
Capivasertib pharmacokinetic parameters are presented as the mean [%coefficient of variation (%CV)], unless otherwise specified. The capivasertib steady-state AUC is 8,069 h·ng/mL (37%) and Cmax is 1,371 ng/mL (30%). Steady-state concentrations are predicted to be attained on the 3rd and 4th dosing day of each week, starting week 2.
Capivasertib plasma concentrations are approximately 0.5% to 15% of the steady state Cmax during the off-dosing days.
Capivasertib AUC and Cmax are proportional with dose over a range of 80 to 800 mg (0.2 to 2 times the approved recommended dosage).
Absorption
Tmax is approximately 1-2 hours. The absolute bioavailability is 29%.
Effect of Food
No clinically meaningful differences in capivasertib pharmacokinetics were observed following administration of TRUQAP with a high-fat meal (approximately 1,000 kcal; fat 60%) or a low-fat meal (approximately 400 kcal; fat 26%).
Distribution
The steady state oral volume of distribution is 1,847 L (36%). Capivasertib plasma protein binding is 22% and the plasma-to-blood ratio is 0.71.
Elimination
The half-life is 8.3 hours and the steady-state oral clearance is 50 L/h (37% CV). Renal clearance was 21% of total clearance.
Metabolism
Capivasertib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and UGT2B7.
Excretion
Following a single radiolabeled oral dose of 400 mg, the mean total recovery was 45% from urine and 50% from feces.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in capivasertib pharmacokinetics were observed based on race/ethnicity (including White, Asian, Black, American Indian or Alaskan Native, and Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander), sex (88% females), body weight (32 to 150 kg), age (26 to 87 years), mild hepatic impairment (bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN or bilirubin >1 to 1.5x ULN), or mild to moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 89 mL/min).
The effect of moderate (bilirubin > 1.5 to 3x ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment is not fully characterized.
TRUQAP has not been studied in patients with severe (bilirubin >3x ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment or severe renal impairment (CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min).
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Effect of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors on Capivasertib: Itraconazole (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) is predicted to increase capivasertib AUC by up to 1.7-fold and Cmax by up to 1.4-fold.
Erythromycin and verapamil (moderate CYP3A inhibitors) are predicted to increase capivasertib AUC by up to 1.5-fold and Cmax by up to 1.3-fold.
Effect of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers on Capivasertib: Rifampicin (strong CYP3A4 inducer) is predicted to decrease capivasertib AUC by 70% and Cmax by 60%.
Efavirenz (moderate CYP3A4 inducer) is predicted to decrease capivasertib AUC by 60% and Cmax by 50%.
Effect of UGT2B7 Inhibitors on Capivasertib: Probenecid (UGT2B7 inhibitor) is not predicted to have a clinically meaningful effect on capivasertib pharmacokinetics.
Effect of Acid Reducing Agents on Capivasertib: Rabeprazole (gastric acid reducing agent) did not have a clinically meaningful effect on capivasertib pharmacokinetics.
Effect of Capivasertib on CYP3A Substrates: Concomitant use of TRUQAP increased midazolam (CYP3A substrate) AUC by 1.8-fold on day 4 and by 1.2-fold on day 7.
Effect of Capivasertib on CYP2D6 Substrates: TRUQAP is predicted to increase desipramine (CYP2D6 substrate) AUC by up to 2.1-fold on day 4.
Effect of Capivasertib on CYP2C9 Substrates: Concomitant use of TRUQAP with warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate) is not predicted to have a clinically meaningful effect on warfarin pharmacokinetics.
Effect of Capivasertib on UGT1A1 Substrates: TRUQAP is predicted to increase raltegravir (UGT1A1 substrate) AUC by up to 1.7-fold on day 4.
In-Vitro Studies
Capivasertib inhibits BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT3, MATE1, MATE2-K, and OCT2.
13.1. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with capivasertib.
Capivasertib was genotoxic in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay through an aneugenic mechanism. Capivasertib was not mutagenic in vitro in a bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or mouse lymphoma gene mutation assay.
In repeat-dose toxicity studies up to 26 weeks duration in rats and 39 weeks duration in dogs, tubular degeneration in the testes and cellular debris in the epididymides were observed at oral capivasertib doses of 100 mg/kg/day in rats and 15 mg/kg/day in dogs (approximately 1 time the human exposure at the recommended dose of 400 mg twice daily based on AUC). In a male fertility study, capivasertib had no effect on fertility in male rats at oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day following 10 weeks of treatment. Effects of capivasertib on female fertility have not been studied in animals.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of TRUQAP with fulvestrant was evaluated in CAPItello-291 (NCT04305496), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial that enrolled 708 adult patients with locally advanced (inoperable) or metastatic HR-positive, HER2-negative (defined as IHC 0 or 1+, or IHC 2+/ISH-) breast cancer of which 289 patients had tumors with eligible PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-alterations. Eligible PIK3CA/AKT1 activating mutations or PTEN loss of function alterations were identified in the majority of FFPE tumor specimens using FoundationOneCDx next-generation sequencing (n=686). All patients were required to have progression on an aromatase inhibitor (AI) based treatment in the metastatic setting or recurrence on or within 12 months of completing (neo)adjuvant treatment with an AI. Patients could have received up to two prior lines of endocrine therapy and up to 1 line of chemotherapy for locally advanced (inoperable) or metastatic disease. Patients were excluded if they had clinically significant abnormalities of glucose metabolism (defined as patients with diabetes mellitus Type 1, Type 2, requiring insulin treatment, or HbA1c ≥8% (63.9 mmol/mol)).
Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive either 400 mg of TRUQAP (n=355) or placebo (n=353), given orally twice daily for 4 days followed by 3 days off treatment each week of 28-day treatment cycle. Fulvestrant 500 mg intramuscular injection was administered on cycle 1 days 1 and 15, and then at day 1 of each subsequent 28-day cycle. Patients were treated until disease progression, or unacceptable toxicity. Randomization was stratified by presence of liver metastases (yes vs. no), prior treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitors (yes vs. no) and geographical region (region 1: US, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and Israel vs region 2: Latin America, Eastern Europe and Russia vs Region 3: Asia).
The major efficacy outcomes were investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) in the overall population, and in the population of patients whose tumors have PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-alterations evaluated according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST), version 1.1. Additional efficacy outcome measures were overall survival (OS), investigator assessed objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR).
A statistically significant difference in PFS was observed in the overall population and the population of patients whose tumors have PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-alteration. An exploratory analysis of PFS in the 313 (44%) patients whose tumors did not have a PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-alteration showed a HR of 0.79 (95% CI: 0.61, 1.02), indicating that the difference in the overall population was primarily attributed to the results seen in the population of patients whose tumors have PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-alteration.
Of the 289 patients whose tumors were PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-altered, the median age was 59 years (range 34 to 90); female (99%); White (52%), Asian (29%), Black (1%), American Indian/Alaska Native (0.7%), other races (17%) and 9% were Hispanic/Latino. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status was 0 (66%) or 1 (34%), and 18% were premenopausal or perimenopausal. Seventy-six percent of patients had an alteration in PIK3CA, 13% had an alteration in AKT1, and 17% had an alteration in PTEN. All patients received prior endocrine-based therapy (100% AI based treatment and 44% received tamoxifen). Seventy-one percent of patients were previously treated with a CDK4/6 inhibitor and 18% received prior chemotherapy for locally advanced (inoperable) or metastatic disease.
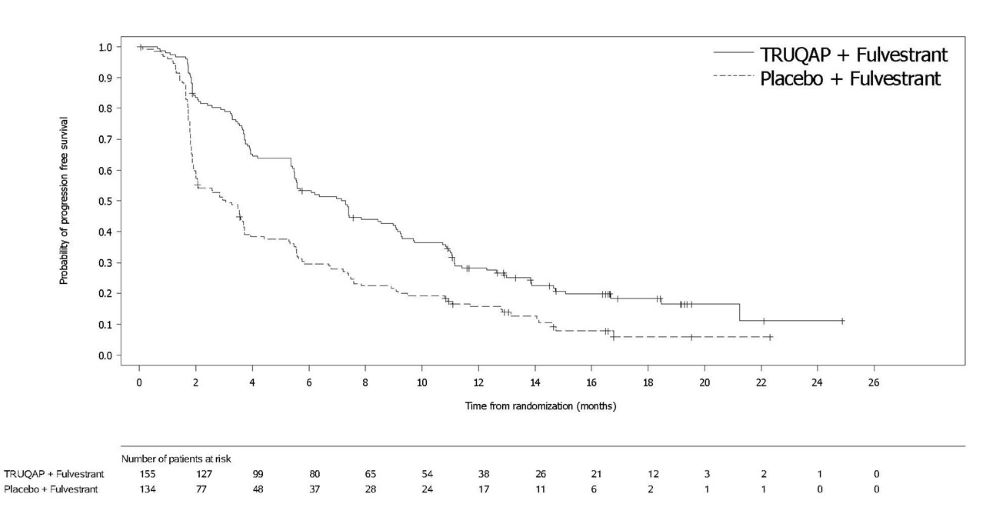
Efficacy results for PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-altered subgroup are presented in Table 7 and Figure 1. Results from the blinded independent review committee (BICR) assessment were consistent with the investigator assessed PFS results. Overall survival results were immature at the time of the PFS analysis (30% of the patients died).
Table 7. Efficacy Results for CAPItello-291 (Patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-Altered Tumors):
| TRUQAP with fulvestrant N=155 | Placebo with fulvestrant N=134 | |
|---|---|---|
| Investigator-Assessed Progression-Free Survival (PFS) | ||
| Number of events (%) | 121 (78%) | 115 (86%) |
| Median, months (95%CI) | 7.3 (5.5, 9.0) | 3.1 (2.0, 3.7) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI)* | 0.50 (0.38, 0.65) | |
| p-value† | <0.0001 | |
| Investigator-Assessed Confirmed Objective Response Rate (ORR) | ||
| Patients with measurable disease | 132 | 124 |
| ORR (95% CI) | 26% (19, 34) | 8% (4, 14) |
| Complete response rate | 2.3% | 0 |
| Partial response rate | 23% | 8% |
| Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 10.2 (7.7, NC‡) | 8.6 (3.8, 9.2) |
* Stratified Cox proportional hazards model stratified by presence of liver metastases (yes vs no), and prior use of CDK4/6 inhibitors (yes vs no).
† Stratified log-rank test stratified by presence of liver metastases (yes vs no), and prior use of CDK4/6 inhibitors (yes vs no).
‡ NC = not calculable
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier Plot of Progression-Free Survival in CAPItello-291 (Investigator Assessment, Patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN-Altered Tumors):
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.