XDEMVY Ophthalmic solution Ref.[107385] Active ingredients: Lotilaner
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2023
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Lotilaner is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-gated chloride channel inhibitor selective for mites. Inhibition of these GABA chloride channels causes a paralytic action in the target organism leading to its death. Lotilaner is not an inhibitor of mammalian GABA mediated chloride channels when tested at up to 30 µM (18 µg/mL) in vitro (approximately 1100 times the RHOD).
12.3. Pharmacokinetics
The systemic pharmacokinetic profile after topical ocular administration was evaluated in healthy volunteers after single and repeat dose administration. The systemic exposure was evaluated in patients at the end of 6 weeks of treatment.
Absorption
Maximum lotilaner concentration was observed 2 hours after a single ocular administration on Day 1 and 1 hour after the last drug administration on Day 42. In healthy subjects, the peak concentration (Cmax) and total exposure (AUC0-12) of lotilaner in whole blood increased after 42 days of repeated ocular administration from 0.596 to 17.8 ng/mL and from 5.75 to 149 hr•ng/mL for Cmax and AUC0-12 respectively. The effective half-life of lotilaner, which is based on the accumulation ratio over the dosing interval of 12 hours, was 264 hours (11 days). In patients with Demodex blepharitis (n=138) who received XDEMVY twice daily for 42 days, the mean (range) systemic exposure at the end of treatment was 12.0 ng/mL (0.4-46.1 ng/mL).
Distribution
Lotilaner plasma protein binding is high (>99.9%) in human plasma. The partitioning of lotilaner to human blood cells is approximately 10% (range 0-20%).
Elimination
The effective half-life in healthy subjects, which is based on the accumulation ratio over the dosing interval of 12 hours, is 264 hours (11 days).
Metabolism
Lotilaner is not metabolized by CYP enzymes.
13.1. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of lotilaner.
Mutagenesis
Lotilaner was not genotoxic in the following assays: Ames assay for bacterial gene mutation, in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes, and in vivo rat micronucleus test.
Impairment of fertility
In a two-generation study of reproductive performance in rats, F0 male and female rats were administered lotilaner at oral doses of 40 mg/kg/day for 80 days reduced to 20 mg/kg/day for 47-50 supplementary days. Reduced pregnancy rates and decreased implantation rates were observed in F0 females at doses 20 mg/kg/day) (approximately 556 times the RHOD on a body surface area basis), which were also associated with maternal toxicity (i.e., decreased body weight and food consumption). No effects on fertility were observed in F0 females at the dose of 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 139 times the MRHOD on a body surface area basis). No effects on fertility were observed in F0 males at the oral dose of 20 mg/kg/day (approximately 556 times the RHOD on a body surface area basis), and no effects on fertility were observed in F1 males and females at the oral dose of 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 139 times the RHOD on a body surface area basis).
14. Clinical Studies
The safety and efficacy of XDEMVY for the treatment of Demodex blepharitis was evaluated in a total of 833 patients (415 of which received XDEMVY) in two 6-week, randomized, multicenter, double-masked, vehicle-controlled studies (Saturn-1 and Saturn-2). Patients with Demodex blepharitis were randomized to either XDEMVY or Vehicle at a 1:1 ratio dosed twice daily in each eye.
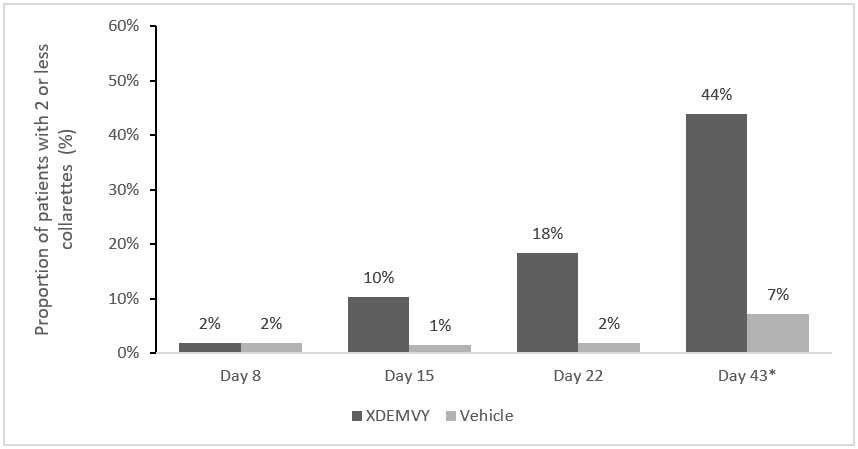
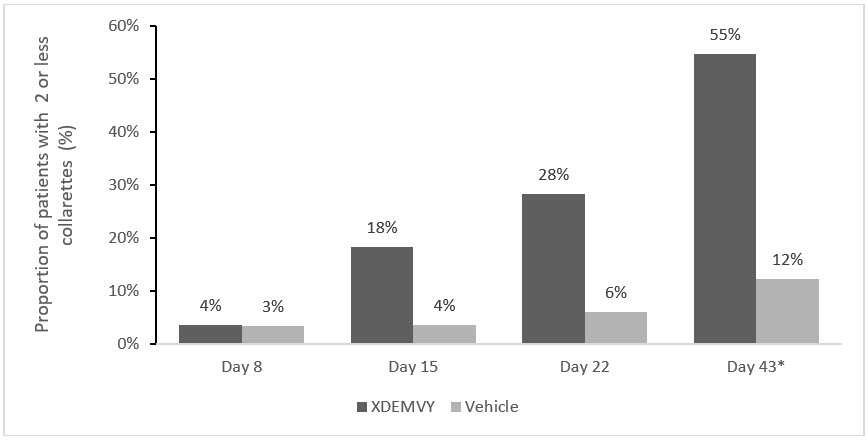
Efficacy was demonstrated by improvement in lids (reduction of collarettes to no more than 2 collarettes per upper lid) in each study (Saturn-1 and Saturn-2) (see Figure 1 and Figure 2) by Day 43.
Figure 1. Saturn-1: Proportion of patients with 2 or less collarettes for the upper eyelid:
* Day 43 Primary Endpoint; XDEMVY N=209, Vehicle N=204, p-value <0.01
Figure 2. Saturn-2: Proportion of patients with 2 or less collarettes for the upper eyelid:
* Day 43 Primary Endpoint; XDEMVY N=193, Vehicle N=200, p-value <0.01
The endpoints of mite eradication (mite density of 0 mites/lash) and erythema cure (Grade 0) of XDEMVY vs. Vehicle demonstrated statistically significant improvement at Day 43 across both Saturn-1 (Table 1) and Saturn-2 (Table 2) studies.
Table 1. Proportion of patients with eradication of Demodex mites and erythema cure in the analysis eye at Day 43 in Saturn-1:
| XDEMVY (N=212) | Vehicle (N=209) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mite Eradication | 68% | 17% | <0.01 |
| Erythema Cure | 19% | 7% | <0.01 |
Table 2. Proportion of patients with eradication of Demodex mites and erythema cure in the analysis eye at Day 43 in Saturn-2:
| XDEMVY (N=203) | Vehicle (N=209) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mite Eradication | 50% | 14% | <0.01 |
| Erythema Cure | 30% | 9% | <0.01 |
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.