ARICEPT Film-coated tablet Ref.[10539] Active ingredients: Donepezil
Source: FDA, National Drug Code (US) Revision Year: 2020
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Current theories on the pathogenesis of the cognitive signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease attribute some of them to a deficiency of cholinergic neurotransmission.
Donepezil hydrochloride is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by acetylcholinesterase. There is no evidence that donepezil alters the course of the underlying dementing process.
12.3. Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics of donepezil are linear over a dose range of 1-10 mg given once daily. The rate and extent of absorption of ARICEPT tablets are not influenced by food.
Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis of plasma donepezil concentrations measured in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, following oral dosing, peak plasma concentration is achieved for ARICEPT 23 mg tablets in approximately 8 hours, compared with 3 hours for ARICEPT 10 mg tablets. Peak plasma concentrations were about 2-fold higher for ARICEPT 23 mg tablets than ARICEPT 10 mg tablets.
ARICEPT ODT 5 mg and 10 mg are bioequivalent to ARICEPT 5 mg and 10 mg tablets, respectively. A food effect study has not been conducted with ARICEPT ODT; however, the effect of food with ARICEPT ODT is expected to be minimal. ARICEPT ODT can be taken without regard to meals.
The elimination half life of donepezil is about 70 hours, and the mean apparent plasma clearance (Cl/F) is 0.13-0.19 L/hr/kg. Following multiple dose administration, donepezil accumulates in plasma by 4-7 fold, and steady state is reached within 15 days. The steady state volume of distribution is 12-16 L/kg. Donepezil is approximately 96% bound to human plasma proteins, mainly to albumins (about 75%) and alpha1-acid glycoprotein (about 21%) over the concentration range of 2-1000 ng/mL.
Donepezil is both excreted in the urine intact and extensively metabolized to four major metabolites, two of which are known to be active, and a number of minor metabolites, not all of which have been identified. Donepezil is metabolized by CYP 450 isoenzymes 2D6 and 3A4 and undergoes glucuronidation. Following administration of 14C-labeled donepezil, plasma radioactivity, expressed as a percent of the administered dose, was present primarily as intact donepezil (53%) and as 6-O-desmethyl donepezil (11%), which has been reported to inhibit AChE to the same extent as donepezil in vitro and was found in plasma at concentrations equal to about 20% of donepezil. Approximately 57% and 15% of the total radioactivity was recovered in urine and feces, respectively, over a period of 10 days, while 28% remained unrecovered, with about 17% of the donepezil dose recovered in the urine as unchanged drug. Examination of the effect of CYP2D6 genotype in Alzheimer’s patients showed differences in clearance values among CYP2D6 genotype subgroups. When compared to the extensive metabolizers, poor metabolizers had a 31.5% slower clearance and ultra-rapid metabolizers had a 24% faster clearance.
Hepatic Disease
In a study of 10 patients with stable alcoholic cirrhosis, the clearance of ARICEPT was decreased by 20% relative to 10 healthy age- and sex-matched subjects.
Renal Disease
In a study of 11 patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (ClC <18 mL/min/1.73 m²) the clearance of ARICEPT did not differ from 11 age- and sex-matched healthy subjects.
Age
No formal pharmacokinetic study was conducted to examine age-related differences in the pharmacokinetics of ARICEPT. Population pharmacokinetic analysis suggested that the clearance of donepezil in patients decreases with increasing age. When compared with 65-year old subjects, 90-year old subjects have a 17% decrease in clearance, while 40-year old subjects have a 33% increase in clearance. The effect of age on donepezil clearance may not be clinically significant.
Gender and Race
No specific pharmacokinetic study was conducted to investigate the effects of gender and race on the disposition of ARICEPT. However, retrospective pharmacokinetic analysis and population pharmacokinetic analysis of plasma donepezil concentrations measured in patients with Alzheimer’s disease indicates that gender and race (Japanese and Caucasians) did not affect the clearance of ARICEPT to an important degree.
Body Weight
There was a relationship noted between body weight and clearance. Over the range of body weight from 50 kg to 110 kg, clearance increased from 7.77 L/h to 14.04 L/h, with a value of 10 L/hr for 70 kg individuals.
Drug Interactions
Effect of ARICEPT on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
No in vivo clinical trials have investigated the effect of ARICEPT on the clearance of drugs metabolized by CYP 3A4 (e.g., cisapride, terfenadine) or by CYP 2D6 (e.g., imipramine). However, in vitro studies show a low rate of binding to these enzymes (mean Ki about 50-130 μM), that, given the therapeutic plasma concentrations of donepezil (164 nM), indicates little likelihood of interference. Based on in vitro studies, donepezil shows little or no evidence of direct inhibition of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP2C19 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Whether ARICEPT has any potential for enzyme induction is not known. Formal pharmacokinetic studies evaluated the potential of ARICEPT for interaction with theophylline, cimetidine, warfarin, digoxin, and ketoconazole. No effects of ARICEPT on the pharmacokinetics of these drugs were observed.
Effect of Other Drugs on the Metabolism of ARICEPT
Ketoconazole and quinidine, strong inhibitors of CYP450 3A and 2D6, respectively, inhibit donepezil metabolism in vitro. Whether there is a clinical effect of quinidine is not known. Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that in the presence of concomitant CYP2D6 inhibitors donepezil AUC was increased by approximately 17% to 20% in Alzheimer’s disease patients taking ARICEPT 10 and 23 mg. This represented an average effect of weak, moderate, and strong CYP2D6 inhibitors. In a 7-day crossover study in 18 healthy volunteers, ketoconazole (200 mg q.d.) increased mean donepezil (5 mg q.d.) concentrations (AUC0-24 and Cmax) by 36%. The clinical relevance of this increase in concentration is unknown.
Inducers of CYP 3A (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, dexamethasone, rifampin, and phenobarbital) could increase the rate of elimination of ARICEPT.
Formal pharmacokinetic studies demonstrated that the metabolism of ARICEPT is not significantly affected by concurrent administration of digoxin or cimetidine.
An in vitro study showed that donepezil was not a substrate of P-glycoprotein.
Drugs Highly Bound to Plasma Proteins
Drug displacement studies have been performed in vitro between this highly bound drug (96%) and other drugs such as furosemide, digoxin, and warfarin. ARICEPT at concentrations of 0.3-10 micrograms/mL did not affect the binding of furosemide (5 micrograms/mL), digoxin (2 ng/mL), and warfarin (3 micrograms/mL) to human albumin. Similarly, the binding of ARICEPT to human albumin was not affected by furosemide, digoxin, and warfarin.
13.1. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No evidence of carcinogenic potential was obtained in an 88-week carcinogenicity study of donepezil conducted in mice at oral doses up to 180 mg/kg/day (approximately 40 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of 23 mg/day on a mg/m² basis), or in a 104-week carcinogenicity study in rats at oral doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 13 times the MRHD on a mg/m² basis).
Donepezil was negative in a battery of genotoxicity assays ( in vitro bacterial reverse mutation, in vitro mouse lymphomatk, in vitro chromosomal aberration, and in vivo mouse micronucleus).
Donepezil had no effect on fertility in rats at oral doses up to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 4 times the MRHD on a mg/m² basis) when administered to males and females prior to and during mating and continuing in females through implantation.
13.2. Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In an acute dose neurotoxicity study in female rats, oral administration of donepezil and memantine in combination resulted in increased incidence, severity, and distribution of neurodegeneration compared with memantine alone. The no-effect levels of the combination were associated with clinically relevant plasma donepezil and memantine levels.
The relevance of this finding to humans is unknown.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease
The effectiveness of ARICEPT as a treatment for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease is demonstrated by the results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical investigations in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (diagnosed by NINCDS and DSM III-R criteria, Mini-Mental State Examination ≥10 and ≤26 and Clinical Dementia Rating of 1 or 2). The mean age of patients participating in ARICEPT trials was 73 years with a range of 50 to 94. Approximately 62% of patients were women and 38% were men. The racial distribution was white 95%, black 3%, and other races 2%.
The higher dose of 10 mg did not provide a statistically significantly greater clinical benefit than 5 mg. There is a suggestion, however, based upon order of group mean scores and dose trend analyses of data from these clinical trials, that a daily dose of 10 mg of ARICEPT might provide additional benefit for some patients. Accordingly, whether or not to employ a dose of 10 mg is a matter of prescriber and patient preference.
Study Outcome Measures
In each study, the effectiveness of treatment with ARICEPT was evaluated using a dual outcome assessment strategy.
The ability of ARICEPT to improve cognitive performance was assessed with the cognitive subscale of the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-cog), a multi-item instrument that has been extensively validated in longitudinal cohorts of Alzheimer’s disease patients. The ADAS-cog examines selected aspects of cognitive performance including elements of memory, orientation, attention, reasoning, language, and praxis. The ADAS-cog scoring range is from 0 to 70, with higher scores indicating greater cognitive impairment. Elderly normal adults may score as low as 0 or 1, but it is not unusual for non-demented adults to score slightly higher.
The patients recruited as participants in each study had mean scores on the ADAS-cog of approximately 26 points, with a range from 4 to 61. Experience based on longitudinal studies of ambulatory patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease suggest that scores on the ADAS-cog increase (worsen) by 6-12 points per year. However, smaller changes may be seen in patients with very mild or very advanced disease since the ADAS-cog is not uniformly sensitive to change over the course of the disease. The annualized rate of decline in the placebo patients participating in ARICEPT trials was approximately 2 to 4 points per year.
The ability of ARICEPT to produce an overall clinical effect was assessed using a Clinician’s Interview-Based Impression of Change that required the use of caregiver information, the CIBIC-plus. The CIBIC-plus is not a single instrument and is not a standardized instrument like the ADAS-cog. Clinical trials for investigational drugs have used a variety of CIBIC formats, each different in terms of depth and structure.
As such, results from a CIBIC-plus reflect clinical experience from the trial or trials in which it was used and cannot be compared directly with the results of CIBIC-plus evaluations from other clinical trials. The CIBIC-plus used in ARICEPT trials was a semi-structured instrument that was intended to examine four major areas of patient function: General, Cognitive, Behavioral, and Activities of Daily Living. It represents the assessment of a skilled clinician based upon his/her observations at an interview with the patient, in combination with information supplied by a caregiver familiar with the behavior of the patient over the interval rated. The CIBIC-plus is scored as a seven-point categorical rating, ranging from a score of 1, indicating “markedly improved”, to a score of 4, indicating “no change” to a score of 7, indicating “markedly worse”. The CIBIC-plus has not been systematically compared directly to assessments not using information from caregivers (CIBIC) or other global methods.
Thirty-Week Study
In a study of 30 weeks duration, 473 patients were randomized to receive single daily doses of placebo, 5 mg/day or 10 mg/day of ARICEPT. The 30-week study was divided into a 24-week double-blind active treatment phase followed by a 6-week single-blind placebo washout period. The study was designed to compare 5 mg/day or 10 mg/day fixed doses of ARICEPT to placebo. However, to reduce the likelihood of cholinergic effects, the 10 mg/day treatment was started following an initial 7-day treatment with 5 mg/day doses.
Effects on the ADAS-cog
Figure 1 illustrates the time course for the change from baseline in ADAS-cog scores for all three dose groups over the 30 weeks of the study. After 24 weeks of treatment, the mean differences in the ADAS-cog change scores for ARICEPT treated patients compared to the patients on placebo were 2.8 and 3.1 points for the 5 mg/day and 10 mg/day treatments, respectively. These differences were statistically significant. While the treatment effect size may appear to be slightly greater for the 10 mg/day treatment, there was no statistically significant difference between the two active treatments.
Following 6 weeks of placebo washout, scores on the ADAS-cog for both the ARICEPT treatment groups were indistinguishable from those patients who had received only placebo for 30 weeks. This suggests that the beneficial effects of ARICEPT abate over 6 weeks following discontinuation of treatment and do not represent a change in the underlying disease. There was no evidence of a rebound effect 6 weeks after abrupt discontinuation of therapy.
Figure 2 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the three treatment groups who had attained the measure of improvement in ADAS-cog score shown on the X axis. Three change scores (7-point and 4-point reductions from baseline or no change in score) have been identified for illustrative purposes, and the percent of patients in each group achieving that result is shown in the inset table.
The curves demonstrate that both patients assigned to placebo and ARICEPT have a wide range of responses, but that the active treatment groups are more likely to show greater improvements. A curve for an effective treatment would be shifted to the left of the curve for placebo, while an ineffective or deleterious treatment would be superimposed upon or shifted to the right of the curve for placebo.
Effects on the CIBIC-plus
Figure 3 is a histogram of the frequency distribution of CIBIC-plus scores attained by patients assigned to each of the three treatment groups who completed 24 weeks of treatment. The mean drug-placebo differences for these groups of patients were 0.35 points and 0.39 points for 5 mg/day and 10 mg/day of ARICEPT, respectively. These differences were statistically significant. There was no statistically significant difference between the two active treatments.
Fifteen-Week Study
In a study of 15 weeks duration, patients were randomized to receive single daily doses of placebo or either 5 mg/day or 10 mg/day of ARICEPT for 12 weeks, followed by a 3-week placebo washout period. As in the 30-week study, to avoid acute cholinergic effects, the 10 mg/day treatment followed an initial 7-day treatment with 5 mg/day doses.
Effects on the ADAS-cog
Figure 4 illustrates the time course of the change from baseline in ADAS-cog scores for all three dose groups over the 15 weeks of the study. After 12 weeks of treatment, the differences in mean ADAS-cog change scores for the ARICEPT treated patients compared to the patients on placebo were 2.7 and 3.0 points each, for the 5 and 10 mg/day ARICEPT treatment groups, respectively. These differences were statistically significant. The effect size for the 10 mg/day group may appear to be slightly larger than that for 5 mg/day. However, the differences between active treatments were not statistically significant.
Following 3 weeks of placebo washout, scores on the ADAS-cog for both the ARICEPT treatment groups increased, indicating that discontinuation of ARICEPT resulted in a loss of its treatment effect. The duration of this placebo washout period was not sufficient to characterize the rate of loss of the treatment effect, but the 30-week study (see above) demonstrated that treatment effects associated with the use of ARICEPT abate within 6 weeks of treatment discontinuation.
Figure 5 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the three treatment groups who attained the measure of improvement in ADAS-cog score shown on the X axis. The same three change scores (7-point and 4-point reductions from baseline or no change in score) as selected for the 30-week study have been used for this illustration. The percentages of patients achieving those results are shown in the inset table.
As observed in the 30-week study, the curves demonstrate that patients assigned to either placebo or to ARICEPT have a wide range of responses, but that the ARICEPT treated patients are more likely to show greater improvements in cognitive performance.
Effects on the CIBIC-plus
Figure 6 is a histogram of the frequency distribution of CIBIC-plus scores attained by patients assigned to each of the three treatment groups who completed 12 weeks of treatment. The differences in mean scores for ARICEPT treated patients compared to the patients on placebo at Week 12 were 0.36 and 0.38 points for the 5 mg/day and 10 mg/day treatment groups, respectively. These differences were statistically significant.
In both studies, patient age, sex, and race were not found to predict the clinical outcome of ARICEPT treatment.
14.2 Moderate to Severe Alzheimer’s Disease
The effectiveness of ARICEPT in the treatment of patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease was established in studies employing doses of 10 mg/day and 23 mg/day. Results of a controlled clinical trial in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s Disease that compared ARICEPT 23 mg once daily to 10 mg once daily suggest that a 23 mg dose of ARICEPT provided additional benefit.
Swedish 6 Month Study (10 mg/day)
The effectiveness of ARICEPT as a treatment for severe Alzheimer’s disease is demonstrated by the results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study conducted in Sweden (6 month study) in patients with probable or possible Alzheimer’s disease diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA and DSM-IV criteria, MMSE: range of 1-10. Two hundred and forty eight (248) patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease were randomized to ARICEPT or placebo. For patients randomized to ARICEPT, treatment was initiated at 5 mg once daily for 28 days and then increased to 10 mg once daily. At the end of the 6 month treatment period, 90.5% of the ARICEPT treated patients were receiving the 10 mg/day dose. The mean age of patients was 84.9 years, with a range of 59 to 99. Approximately 77% of patients were women, and 23% were men. Almost all patients were Caucasian. Probable Alzheimer’s disease was diagnosed in the majority of the patients (83.6% of ARICEPT treated patients and 84.2% of placebo treated patients).
Study Outcome Measures
The effectiveness of treatment with ARICEPT was determined using a dual outcome assessment strategy that evaluated cognitive function using an instrument designed for more impaired patients and overall function through caregiver-rated assessment. This study showed that patients on ARICEPT experienced significant improvement on both measures compared to placebo.
The ability of ARICEPT to improve cognitive performance was assessed with the Severe Impairment Battery (SIB). The SIB, a multi-item instrument, has been validated for the evaluation of cognitive function in patients with moderate to severe dementia. The SIB evaluates selective aspects of cognitive performance, including elements of memory, language, orientation, attention, praxis, visuospatial ability, construction, and social interaction. The SIB scoring range is from 0 to 100, with lower scores indicating greater cognitive impairment.
Daily function was assessed using the Modified Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Activities of Daily Living Inventory for Severe Alzheimer’s Disease (ADCS-ADL-severe). The ADCS-ADL-severe is derived from the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Activities of Daily Living Inventory, which is a comprehensive battery of ADL questions used to measure the functional capabilities of patients. Each ADL item is rated from the highest level of independent performance to complete loss. The ADCS-ADL-severe is a subset of 19 items, including ratings of the patient’s ability to eat, dress, bathe, use the telephone, get around (or travel), and perform other activities of daily living; it has been validated for the assessment of patients with moderate to severe dementia. The ADCS-ADL-severe has a scoring range of 0 to 54, with the lower scores indicating greater functional impairment. The investigator performs the inventory by interviewing a caregiver, in this study a nurse staff member, familiar with the functioning of the patient.
Effects on the SIB
Figure 7 shows the time course for the change from baseline in SIB score for the two treatment groups over the 6 months of the study. At 6 months of treatment, the mean difference in the SIB change scores for ARICEPT treated patients compared to patients on placebo was 5.9 points. ARICEPT treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Figure 8 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the two treatment groups who attained the measure of improvement in SIB score shown on the X-axis. While patients assigned both to ARICEPT and to placebo have a wide range of responses, the curves show that the ARICEPT group is more likely to show a greater improvement in cognitive performance.
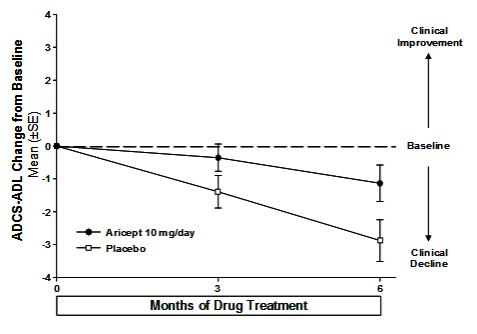
Effects on the ADCS-ADL-severe
Figure 9 illustrates the time course for the change from baseline in ADCS-ADL-severe scores for patients in the two treatment groups over the 6 months of the study. After 6 months of treatment, the mean difference in the ADCS-ADL-severe change scores for ARICEPT treated patients compared to patients on placebo was 1.8 points. ARICEPT treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Figure 10 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each treatment group with specified changes from baseline ADCS-ADL-severe scores. While both patients assigned to ARICEPT and placebo have a wide range of responses, the curves demonstrate that the ARICEPT group is more likely to show a smaller decline or an improvement.
Japanese 24-Week Study (10 mg/day)
In a study of 24 weeks duration conducted in Japan, 325 patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease were randomized to doses of 5 mg/day or 10 mg/day of donepezil, administered once daily, or placebo. Patients randomized to treatment with donepezil were to achieve their assigned doses by titration, beginning at 3 mg/day, and extending over a maximum of 6 weeks. Two hundred and forty eight (248) patients completed the study, with similar proportions of patients completing the study in each treatment group. The primary efficacy measures for this study were the SIB and CIBIC-plus.
At 24 weeks of treatment, statistically significant treatment differences were observed between the 10 mg/day dose of donepezil and placebo on both the SIB and CIBIC-plus. The 5 mg/day dose of donepezil showed a statistically significant superiority to placebo on the SIB, but not on the CIBIC-plus.
Study of 23 mg/day
The effectiveness of ARICEPT 23 mg/day as a treatment for moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease has been demonstrated by the results of a randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical investigation in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. The controlled clinical study was conducted globally in patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA and DSM-IV criteria, MMSE: range of 0-20. Patients were required to have been on a stable dose of ARICEPT 10 mg/day for at least 3 months prior to screening. One thousand four hundred and thirty four (1434) patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease were randomized to 23 mg/day or 10 mg/day. The mean age of patients was 73.8 years, with a range of 47 to 90. Approximately 63% of patients were women, and 37% were men. Approximately 36% of the patients were taking memantine throughout the study.
Study Outcome Measures
The effectiveness of treatment with 23 mg/day was determined using a dual outcome assessment strategy that evaluated cognitive function using an instrument designed for more impaired patients and overall function through caregiver-rated assessment.
The ability of 23 mg/day to improve cognitive performance was assessed with the Severe Impairment Battery (SIB). The SIB, a multi-item instrument, has been validated for the evaluation of cognitive function in patients with moderate to severe dementia. The SIB evaluates selective aspects of cognitive performance, including elements of memory, language, orientation, attention, praxis, visuospatial ability, construction, and social interaction. The SIB scoring range is from 0 to 100, with lower scores indicating greater cognitive impairment.
The ability of 23 mg/day to produce an overall clinical effect was assessed using a Clinician’s Interview-Based Impression of Change that incorporated the use of caregiver information, the CIBIC-plus. The CIBIC-plus used in this trial was a semi-structured instrument that examines four major areas of patient function: General, Cognitive, Behavioral, and Activities of Daily Living. It represents the assessment of a skilled clinician based upon his/her observations at an interview with the patient, in combination with information supplied by a caregiver familiar with the behavior of the patient over the interval rated. The CIBIC-plus is scored as a seven-point categorical rating, ranging from a score of 1, indicating “markedly improved”, to a score of 4, indicating “no change” to a score of 7, indicating “markedly worse”.
Effects on the SIB
Figure 11 shows the time course for the change from baseline in SIB score for the two treatment groups over the 24 weeks of the study. At 24 weeks of treatment, the LS mean difference in the SIB change scores for 23 mg/day-treated patients compared to patients treated with 10 mg was 2.2 units (p=0.0001). The dose of 23 mg/day was statistically significantly superior to the dose of 10 mg/day.
Figure 12 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the two treatment groups who attained the measure of improvement in SIB score shown on the X-axis. While patients assigned both to 23 mg/day and to 10 mg/day have a wide range of responses, the curves show that the 23 mg-group is more likely to show a greater improvement in cognitive performance. When such curves are shifted to the left, this indicates a greater percentage of patients responding to treatment on the SIB.
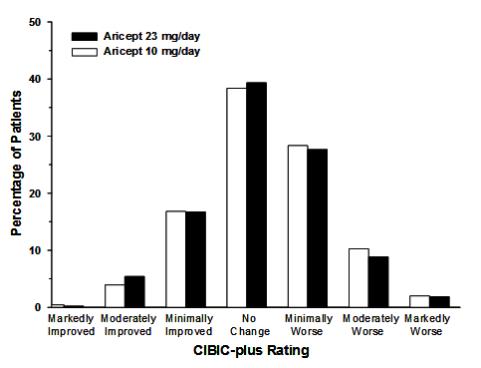
Effects on the CIBIC-plus
Figure 13 is a histogram of the frequency distribution of CIBIC-plus scores attained by patients at the end of 24 weeks of treatment. The mean difference between the 23 mg/day and 10 mg/day treatment groups was 0.06 units. This difference was not statistically significant.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.