FIBRYGA Powder and solvent for solution for injection/infusion Ref.[27529] Active ingredients: Human fibrinogen
Source: Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (GB) Revision Year: 2021 Publisher: Octapharma Ltd., The Zenith Building, 26 Spring Gardens, Manchester M2 1AB, United Kingdom
4.1. Therapeutic indications
Treatment of bleeding and peri-operative prophylaxis in patients with congenital hypo- or afibrinogenaemia with bleeding tendency.
As complementary therapy to management of uncontrolled severe haemorrhage in patients with acquired hypofibrinogenaemia in the course of surgical intervention.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of coagulation disorders.
Posology
The dosage and duration of the substitution therapy depend on the severity of the disorder, location and extent of bleeding and the patient’s clinical condition.
The (functional) fibrinogen level should be determined in order to calculate individual dosage and the amount and frequency of administration should be determined on an individual patient basis by regular measurement of plasma fibrinogen level and continuous monitoring of the clinical condition of the patient and other replacement therapies used.
In case of major surgical intervention, precise monitoring of replacement therapy by coagulation assays is essential.
1. Prophylaxis in patients with congenital hypo- or afibrinogenaemia and known bleeding tendency
To prevent excessive bleeding during surgical procedures, prophylactic treatment is recommended to raise fibrinogen levels to 1 g/L and maintain fibrinogen at this level until haemostasis is secured and above 0.5 g/L until wound healing is complete.
In case of surgical procedure or treatment of a bleeding episode, the dose should be calculated as follows:
Subsequent posology (doses and frequency of injections) should be adapted based on the patient’s clinical status and laboratory results.
The biological half-life of fibrinogen is 3-4 days. Thus, in the absence of consumption, repeated treatment with human fibrinogen is not usually required. Given the accumulation that occurs in case of repeated administration for a prophylactic use, the dose and the frequency should be determined according to the therapeutic goals of the physician for a given patient.
Posology in specific populations
Paediatric Patients:
Currently available data are described in section 4.8 and 5.1 but no recommendation on a posology can be made in children.
Elderly patients:
Clinical studies of FIBRYGA did not include patients aged 65 years and over to provide conclusive evidence as to whether or not they respond differently than younger patients.
2. Treatment of bleeding
Bleeding in patients with congenital hypo- or afibrinogenaemia
Bleeding should be treated to achieve a recommended target fibrinogen plasma level of 1 g/L. This level should be maintained until haemostasis is secured.
Bleeding in patients with acquired fibrinogen deficiency
Adults:
Generally 1-2 g is administered initially with subsequent infusions as required. In case of severe haemorrhage e.g. major surgery, larger amounts (4-8 g) of fibrinogen may be required.
Children:
The dosage should be determined according to the body weight and clinical need but is usually 20-30 mg/kg.
Method of administration
Intravenous infusion or injection.
FIBRYGA should be administered slowly intravenously at a recommended maximum rate of 5 mL per minute for patients with congenital hypo- or afibrinogenaemia and at a recommended maximum rate of 10 mL per minute for patients with acquired fibrinogen deficiency.
For instructions on reconstitution of the medicinal product before administration, see section 6.6.
4.9. Overdose
In order to avoid overdose, regular monitoring of the plasma level of fibrinogen during therapy is indicated (see 4.2).
In case of overdose, the risk of development of thromboembolic complications is enhanced.
6.3. Shelf life
2 years.
The chemical and physical in-use stability of the reconstituted solution has been demonstrated for 24 hours at room temperature (max. 25°C). From a microbiological point of view the product should be used immediately after reconstitution. If not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user. The reconstituted solution must not be frozen or stored in a refrigerator. Partially used bottles should be discarded.
6.4. Special precautions for storage
Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze. Keep the bottle in the outer carton to protect from light.
For storage conditions after reconstitution of the medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5. Nature and contents of container
Each pack contains:
- 1g human fibrinogen in a 100 mL colorless glass bottle, Type II Ph.Eur., sealed with an infusion stopper (bromobutyl rubber) and an aluminium flip-off cap.
- 50 mL solvent (water for injections) in a 50 mL colorless glass vial, Type II Ph.Eur., sealed with an infusion stopper (halobutyl rubber) and an aluminium flip-off cap
- 1 Octajet transfer device
- 1 particle filter
6.6. Special precautions for disposal and other handling
General Instructions
The reconstituted solution should be almost colorless and slightly opalescent. Do not use solutions that are cloudy or have deposits.
Reconstitution
1. Warm both the powder (FIBRYGA) and the solvent (WFI)in unopened containers up to room temperature. This temperature should be maintained during reconstitution. If a water bath is used for warming, care must be taken to avoid water coming into contact with the rubber stoppers or the caps of the containers. The temperature of the water bath should not exceed +37°C (98°F).
2. Remove the cap from the powder (FIBRYGA) bottle and the solvent to expose the central portion of the infusion stopper. Clean the rubber stoppers with an alcohol swab and allow the rubber stoppers to dry.
3. Peel away the lid of the outer package of the Octajet transfer device. To maintain sterility, leave the Octajet device in the clear outer packaging.
4. Take the Octajet in its outer package and invert it over the powder (FIBRYGA) bottle. Place device while in the outer package onto the center of the powder bottle until the clips of the product spike (colorless) are locked. While holding onto the powder bottle, carefully remove the outer package from the Octajet, being careful to not touch the water spike (blue) and leave the Octajet attached firmly to the powder bottle. (Fig. 1)
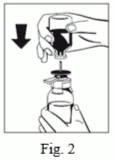
5. With the powder (FIBRYGA) bottle held firmly on a level surface, invert the solvent vial and place it at the center of the water spike. Push the blue plastic spike of the Octajet firmly through the rubber stopper of the solvent vial. (Fig. 2)
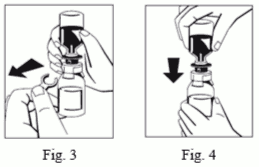
6. Remove the distance ring (Fig. 3) and press the solvent vial down (Fig. 4). Solvent will flow into the powder (FIBRYGA) bottle.
7. When transfer of the solvent is complete, gently swirl the product bottle until the powder is fully dissolved. Do not shake the bottle to avoid foam formation. The powder should be dissolved completely within approximately 5 minutes. It should not take longer than 30 minutes to dissolve the powder. If the powder is not dissolved within 30 minutes the product should be discarded.
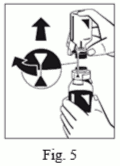
8. Turn the blue solvent vial connector (both directions possible) to bring position markers together and remove solvent vial together with the water spike. (Fig. 5)
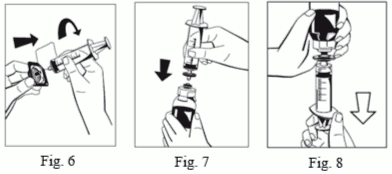
9. Attach a syringe to the provided filter (Fig. 6) and connect the filter to the Octajet Luer Lock on the powder bottle (Fig. 7). Withdraw the solution through the filter into the syringe. (Fig. 8)
10. Detach the filled syringe from the filter and discard the empty bottle.
A standard infusion set is recommended for intravenous application of the reconstituted solution at room temperature.
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
© All content on this website, including data entry, data processing, decision support tools, "RxReasoner" logo and graphics, is the intellectual property of RxReasoner and is protected by copyright laws. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of any part of this content without explicit written permission from RxReasoner is strictly prohibited. Any third-party content used on this site is acknowledged and utilized under fair use principles.